Check Drift concept
Published 14 March 2024
Check Drift Concept
Overview
The -drift flag produces a report indicating differences between structure of your target database and structure created by the migrations applied by Flyway.
Configuring the environment
Please see the check -drift parameter reference page
Examples
There are a variety of ways to configure Flyway to produce this report so we'll step through a couple and show you what it is doing along the way.
Example: environment and buildEnvironment
The check -drift command and flag works by building a temporary database. This 'build' environment that contains a 'build' database is made to reflect the state of your target schema based on the migrations applied by Flyway.
The difference between the two states of this build database and your target database represents the drift between the expected structure according to Flyway and the actual structure. This difference is captured as an artefact called a "Drift Report". The drift report is available as both HTML (human readable) and JSON (machine readable) formats.
The process works like this:
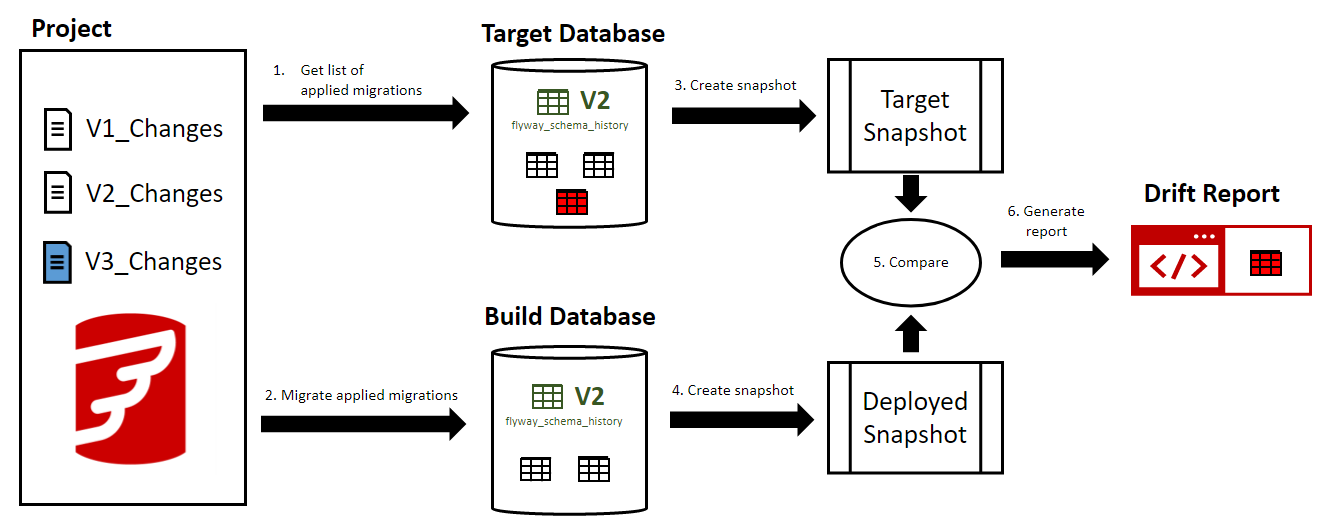
- Specify your target database location
- This is the database you want to apply your changes to, where Flyway is already being used to manage migrations (ie. A Flyway migrations table exists)
- Specify a build database
- This is an existing build database (note: Flyway will "clean" this database, so if you specify a full database, you must ensure it is ok to for Flyway to erase its schema)
- Run
flyway check -drift -check.buildEnvironment="build" -environment="production"
Flyway's check -drift will then:
- Take a
snapshotof the target database - Clean your build database
- Query the target database for the list of applied migrations (for simplicity, let's say it's at V2)
- Apply these migrations to the build database
- Take a
snapshotof the build database (now also at V2) - Compare the V2 target database snapshot to the V2 build database snapshot
- Generate a HTML (human readable) and JSON (machine readable) Drift Report, indicating the additions, deletions, and modifications of database objects between target and build




