Tutorial - Configure the shadow database
Published 11 October 2021
- If no shadow database is configured, you will be prompted to configure it from the GUI when navigating to the Generate Migrations tab.
- If 'Guided Shadow Provisioning' preview feature is enabled, see instructions for this in the section below
- If 'Guided Shadow Provisioning' preview feature is not enabled, continue by entering the connection details for your shadow database, including authentication type and credentials.
- By default, your password is stored in your operating systems built-in credential storage tool.
- By default, your shadow database information is stored to the user settings.
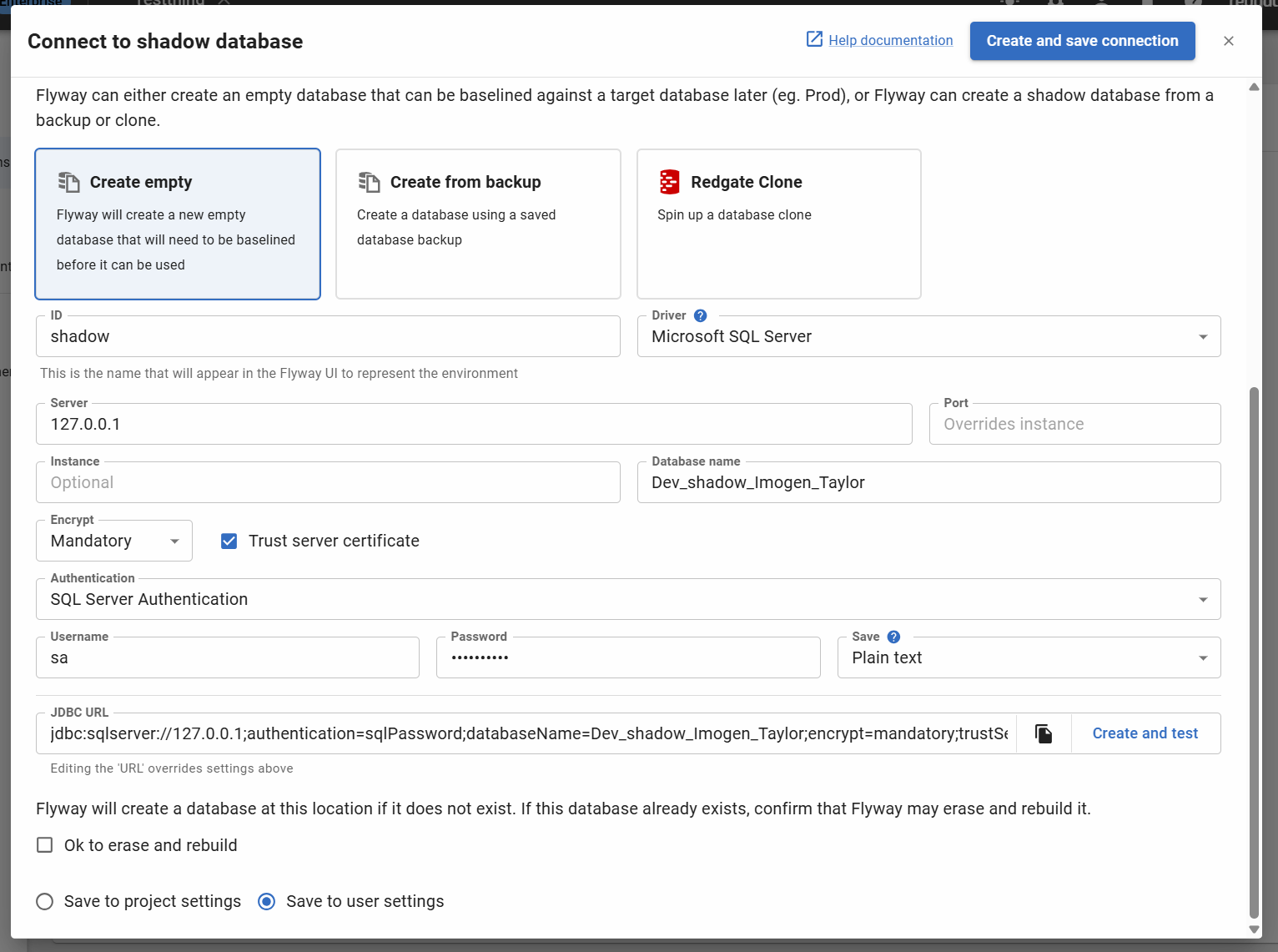
When setting the shadow database/schema connection, ensure it isn't an important database/schema as this may be cleaned and rebuilt when generating migration scripts in Flyway Desktop. There is a checkbox that you must explicitly click to confirm that all the data and schema in the shadow database can be erased. You will also need to make sure that you have sufficient permissions to clean the database/schema.
- Click Test connection or Test and save to close the dialog and start tracking changes to your development database.
- Once it is configured, the connection details can be altered via the Environments page or the Settings Cog, which will display the following options.
Guided Shadow Provisioning - have Flyway create shadow database for you in SQL Server Projects
Status: Preview
Guided Shadow Configuration is a new process to help Flyway Desktop users set up a shadow database as quickly and efficiently as possible. With this, Flyway can create a shadow database for you, and you can customize default values if needed. If you have an existing database you can also connect to this through the dialog using the 'Manually configure existing database' option.
Prerequisites
- You must be using a SQL Server project - other database types coming soon!
- Preview feature “Guided Shadow Provisioning” must be enabled in the Preview features menu
- Have a Development database configured in your project, and we would recommend populating the schema model
- Ensure Flyway has sufficient user permissions to clean and create the shadow database
Creating the Shadow Database
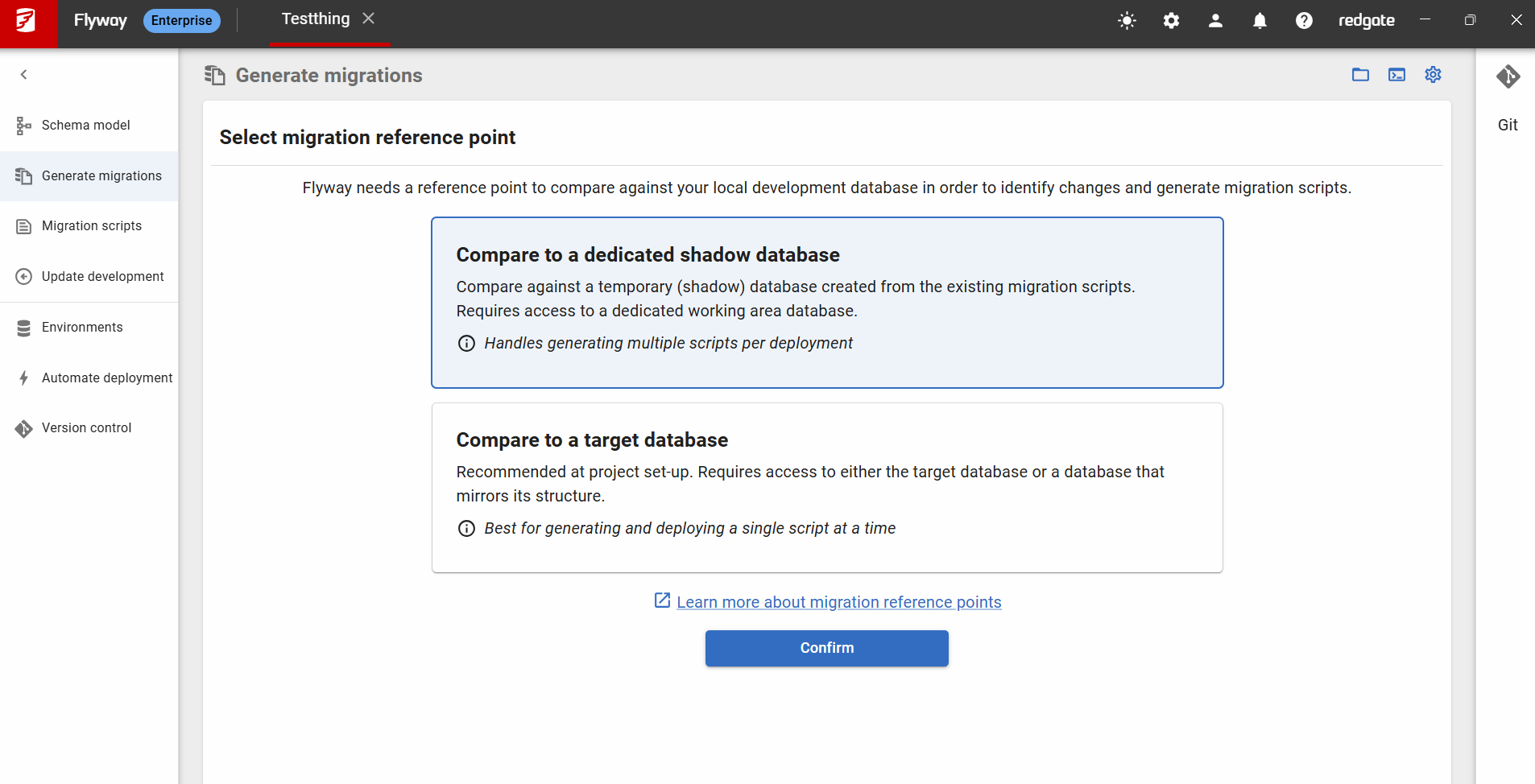
If you do not yet have a Shadow Database configured when going to the “Generate Migrations” page you will see the following choices:
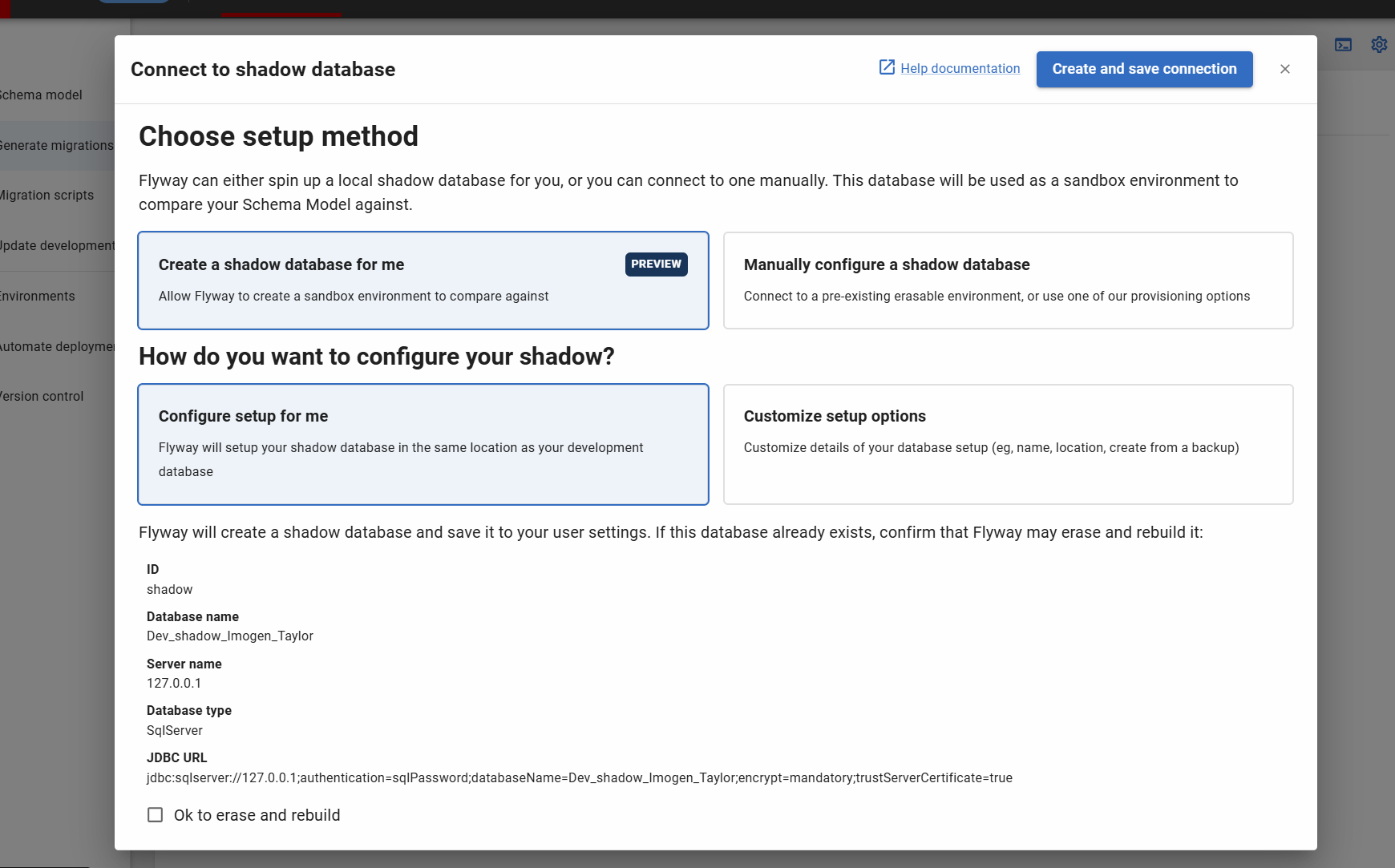
After clicking “Confirm” for the 'Compare to a dedicated shadow database' option, you will be taken to the configuration dialog:
- This screen shows the default settings for the database Flyway will create. By default, this is a database created in same location as your Development database, with name “[current_dev_db]_shadow_[your_username]”
- You must check 'Ok to erase and rebuild' to confirm you are happy for Flyway to clean the database during the reprovision step
- Clicking on 'Create and save connection' will automatically create the database with the above details and save your connection to your current project user settings
If a database with the same name exists already, clicking 'Create and save connection' may result in Flyway erasing the data in your database and rebuilding it. If you want to connect an existing database, use the 'Manually configure a shadow database' option
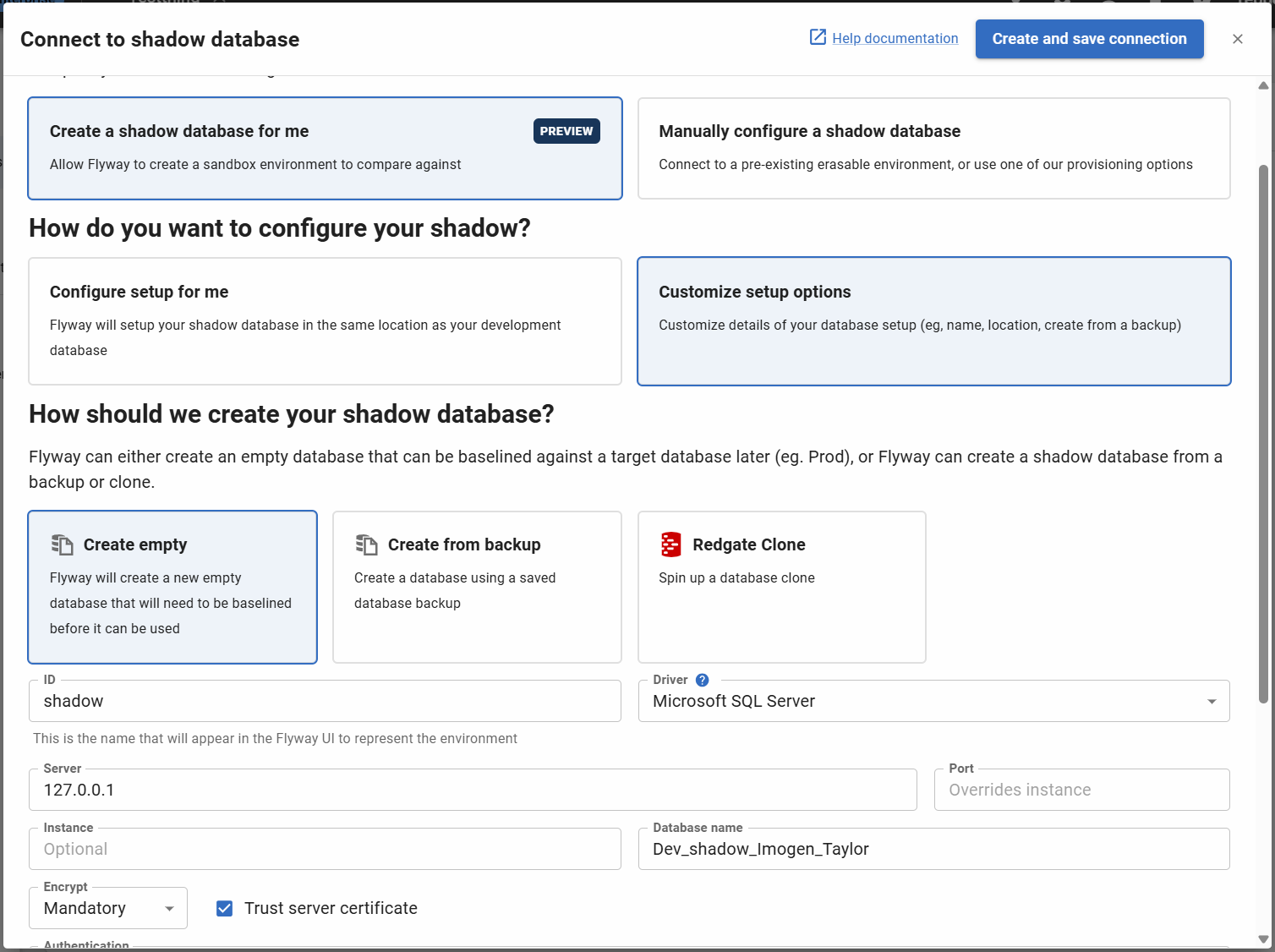
Customization options
- Clicking on 'Customize setup options' will let you change the default settings, or use a different provisioner
- You must check 'Ok to erase and rebuild' to confirm that you are happy for Flyway clean the database during the reprovision step
You can add a shadow database environment configuration to your toml configuration file or user configuration file as follows:
|
TOML Configuration for creating user specific shadow databases
If all of your developers have the same shadow connection details, this can be saved in the flyway.toml project file to make setup easier. Just save the database details to the project settings, which are stored in the flyway.toml project file and gets committed and shared in version control. For example, every developer has 2 databases (projectName and projectName_shadow) on their localhost.
If you are using a shared server for your shadow database, the project can be setup to create a shadow database for each user in the flyway.toml project file using the UserName environment variable on Windows. Make sure to update the provisioner to be "create-database" so this database will be created as new team members join the project. The user would need to have permissions to create a database on the server for this to work
|
${env.UserName:a} gets expanded to the user's username. :a removes any non-ASCII characters so special characters in a name are not a concern. For example, this would create a database named projectName_shadow_myUserName.
Hint - start your shadow database names with a z
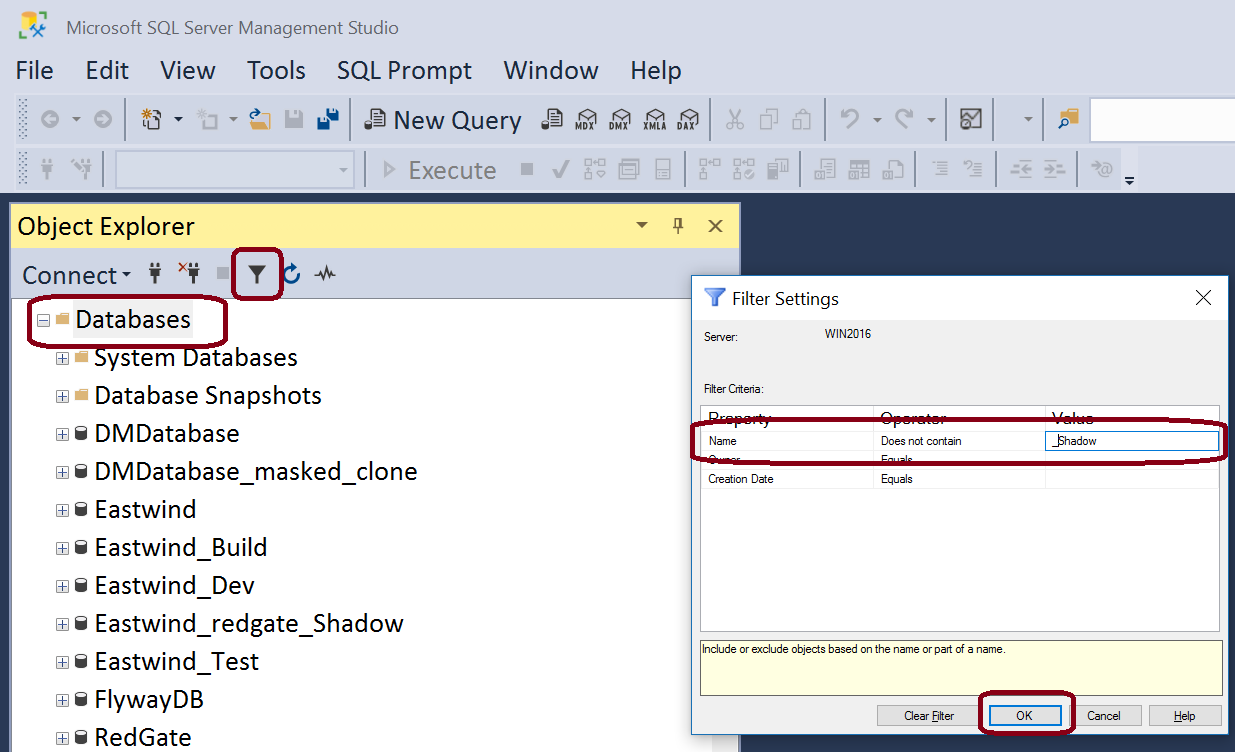
Some users like to name their shadows as z_<DbName>_shadow_<DevName>. This is especially true on a shared centralized development server so all these databases appear at the end of the list. If you are using SQL Server and SSMS, you can filter out and databases whose name contain "_shadow" from the Object Explorer view.
Next steps
Pick one of:
- Validate migration deployment
- Generate migrations (note that this validates migration deployment as part of comparing against migrations)
- Baseline (prerequisite for generating migrations if you do not have any yet, unless working on a completely greenfield database)