Adding SQL Server on Windows
Published 28 March 2024
Monitoring SQL Server instances running on Windows is only supported from Base Monitors running on Windows.
This page explains how to add SQL Server instances, running on Windows machines.
- Go to the Configuration page and, under Estate, select Monitored servers.
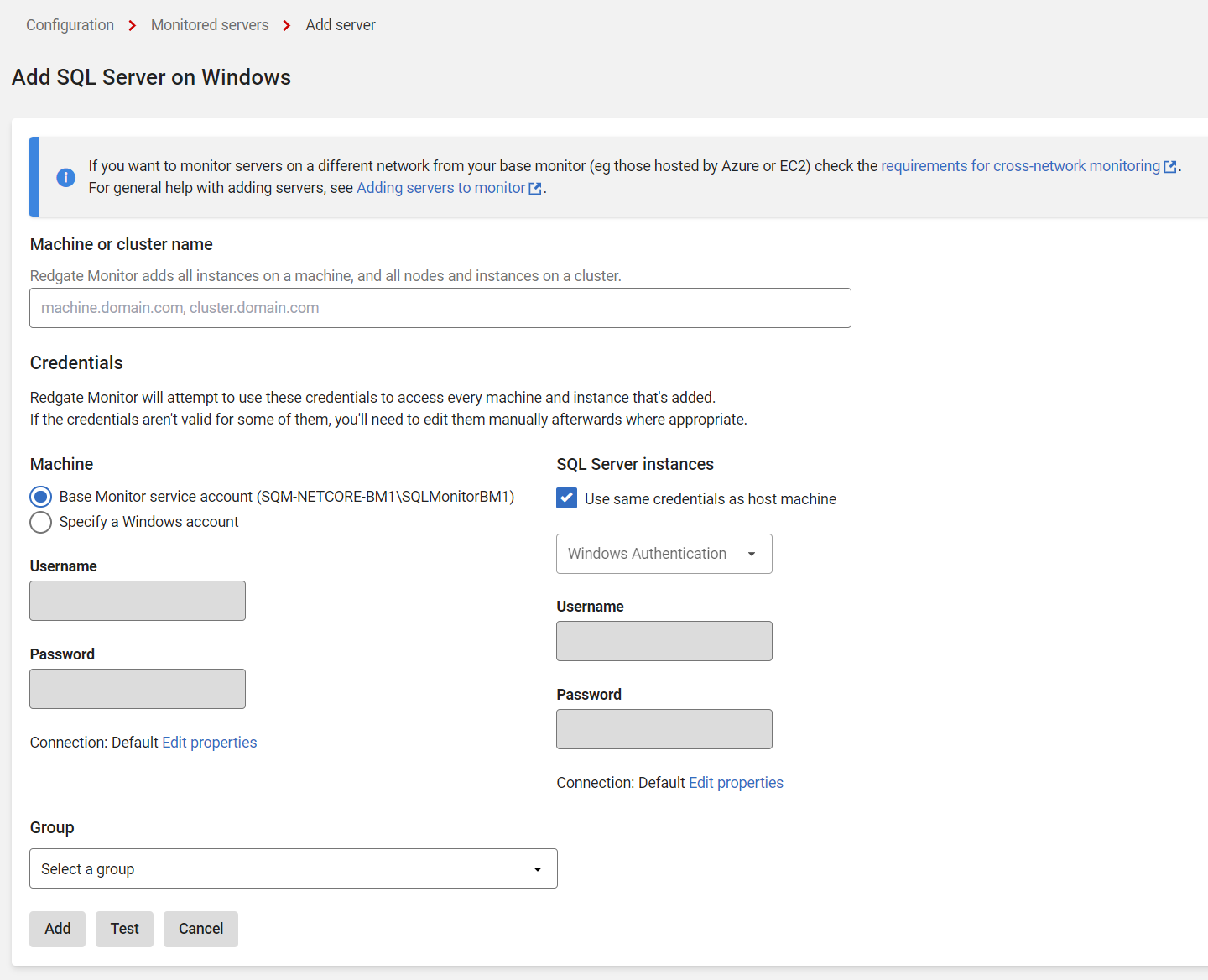
- Click Add > SQL Server on Windows. The Add SQL Server panel expands:
In the machine or cluster name field, enter the server(s) you want to monitor.
Adding instances on non-clustered machines
To add instances on a non-clustered machine, enter the machine name.
Redgate Monitor adds all the instances that are running on the machine (it doesn't add instances that are disabled or not started).
Adding failover cluster instances and standalone instances on clusters
To add instances on a cluster, including standalone instances installed on the cluster's nodes, enter [cluster-name] or [node-name] (where [node-name] is any node in the cluster).
Redgate Monitor adds all the failover cluster instances on a cluster, but only adds the standalone instances that are running (it doesn't add standalone instances that are disabled or not started).
You can no longer add or remove specific instances. To stop monitoring a specific instance, go to Actions > Suspend monitoring.
When you enter [cluster-name] or [node-name], Redgate Monitor will add the cluster and all nodes in the cluster. If you enter [node-name] and the node is in a cluster, make sure the cluster name is routable.
If you add new instances or nodes to a cluster you are already monitoring, Redgate Monitor will automatically detect and monitor these additions.
Availability groups
If you enter [cluster-name] or [node-name], and your cluster contains availability groups, Redgate Monitor will also monitor these availability groups. They won’t show up on the Monitored servers page, but you’ll receive alerts for them and you'll be able to see them on the overview pages.
You can also enter an [availability-group-listener] instead of the [cluster-name] or [node-name].
When you enter the availability group listener, you don't need to specify the port number.
Providing connection details
- You will need to provide two sets of credentials to connect to:
- The host Windows machine on which the instance is running.
- The SQL Server instance.
By default, Redgate Monitor uses the Base Monitor Service account for both sets of credentials. This is the Windows account you specified during installation to connect to the Data Repository (the SQL Server database that stores all collected data). You can specify a different account to use to connect to the host Windows machine and to the SQL Server instance.
Redgate Monitor will attempt to use these credentials to access every server you add. If the credentials aren't valid for some servers, you'll need to manually edit them after you've added the servers.
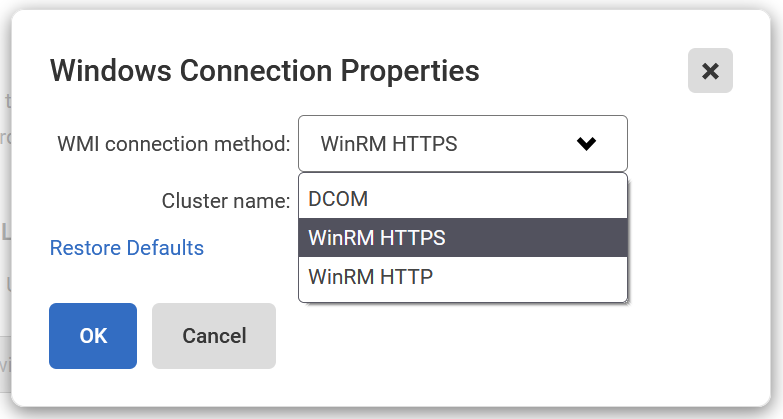
- The Windows connection can be configured to use a different WMI connection method. Click Edit properties in the Machine section.
The Windows Connection Properties dialog opens:
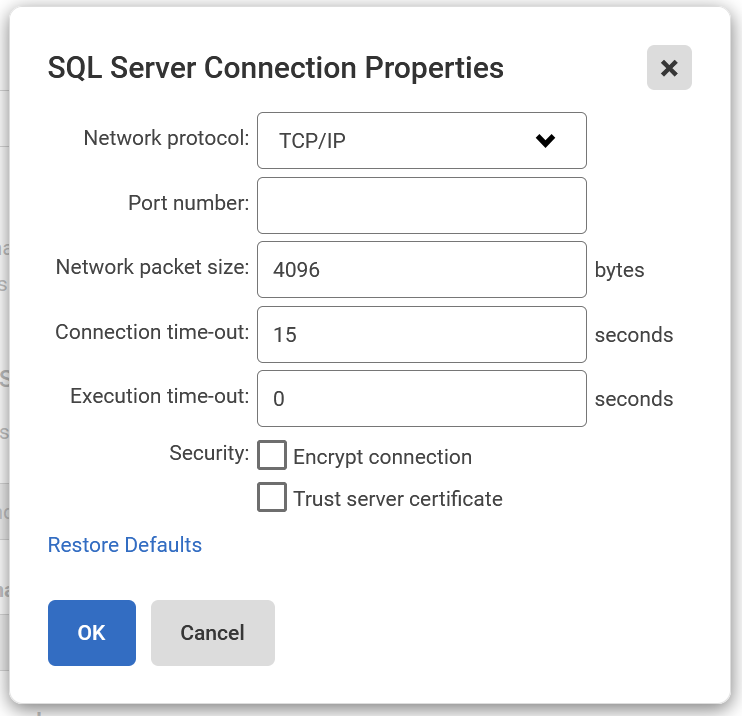
Refer to WMI over WinRM for details on configuring Windows to support WMI over WinRM. - To set more advanced properties (e.g., to connect to a SQL server on a different port), click Edit properties in the SQL Server section.
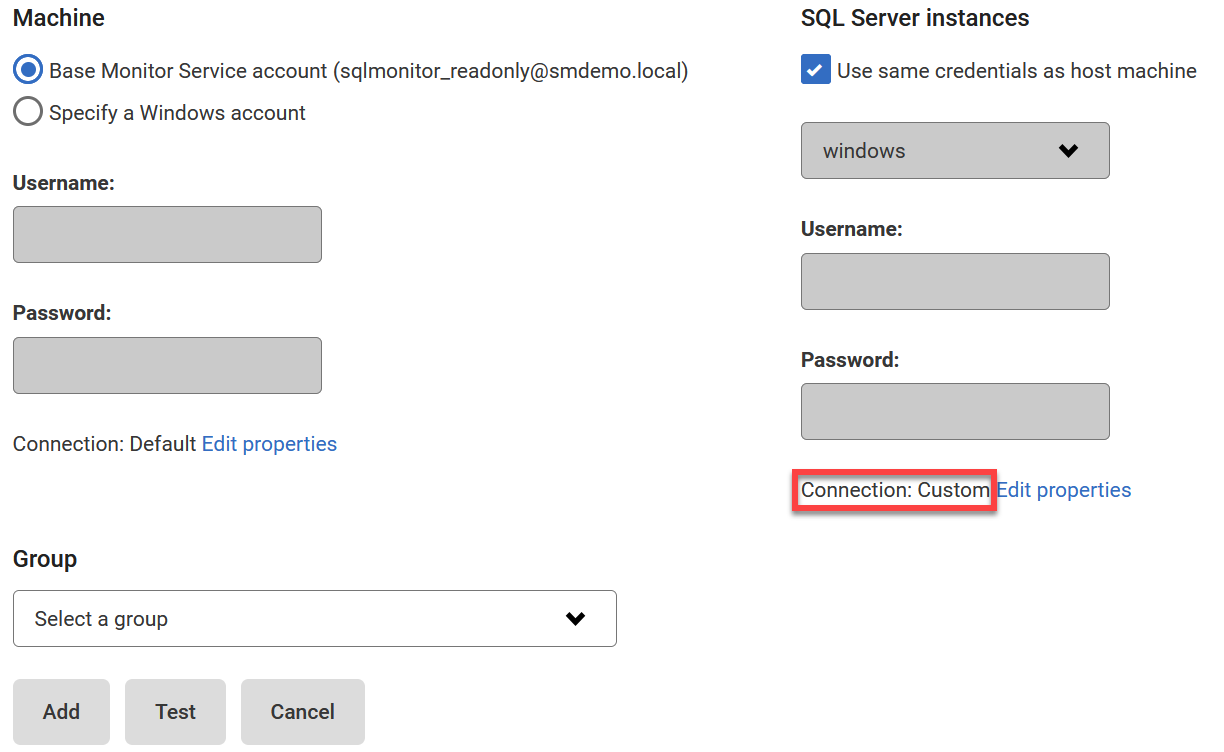
The SQL Server Connection Properties dialog opens: - Enter the properties you want to change for this instance and click OK. If you change the connection properties, they are identified as Custom:
The connection properties persist until you move to a different page in Redgate Monitor. If you add more servers, they will use the custom connection properties.
When you click Add, Redgate Monitor attempts to add the host machine and instance(s) to the list of monitored servers:
Once added, server names can't be edited. If you typed the name incorrectly, the server will be added with a status of "Connection failed (Unreachable)". To fix this, remove the server and add it again.Once a connection is established and a data collection event succeeded, the status is displayed as Monitoring (Connected). If Redgate Monitor encounters a problem and displays a different status, see Monitoring status explained.
Editing the credentials or properties of monitored servers
See Managing Monitored Servers.