Setting up email notification
Published 03 December 2012
About email notification
You can set up SQL Monitor to send an email whenever an alert is raised.
Notification behavior is entirely configurable. You can set up SQL Monitor to:
- send an email for every type of alert
- not send emails at all
- send emails only for those alerts you consider important
Once you have set up your basic email notification settings, you can also tweak email notifications at a more granular level - to use a different recipient for an alert on a particular server, for example, or disable notifications for one or more types of alert.
What is in the email?
Each email message sent by SQL Monitor contains information to help you understand what the problem is before you log in to view details of the alert. This includes:
- the machine and object against which it has been raised
- the alert type and level it was raised at
- the unique ID number that forms part of the URL for this alert
- a hyperlink so that you can open this alert in your browser
Emails sent when a Job failed or Job backup overdue alert is raised will also contain the job name.
If you send emails to other people, they will be prompted for the SQL Monitor password when they follow the link.
When does SQL Monitor send emails?
Each time an alert is raised, it is considered an occurrence of that type of alert, and triggers an email (if email notification is enabled for that type of alert and for that monitored object). For example, if 200 deadlocks occur on one of your instances, 200 emails will be sent, one for each raised alert.
Some types of alerts are continuous (they are raised as Active) and can have a duration. For example, a Backup overdue alert is considered Active until the backup is performed. In this case, only a single email will be sent when the problem is first detected. If the problem escalates, you can choose to receive further emails. See the Also send emails when section below.
Limiting the number of emails sent by SQL Monitor
SQL Monitor limits the number of emails sent to ensure it does not flood your mail servers. It will not send more than 1000 emails per 24 hour period. If this limit is reached, a warning email is sent with advice on how to reduce the volume of emails. This limit is for all emails sent by SQL Monitor, regardless of recipient.
The warning email also contains instructions for adjusting the daily email limit.
To set up email notification
Go to the Configuration tab. Under Alerts and metrics, select Email settings:
Enabling or disabling all emails
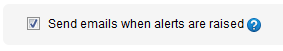
If you want to use email notification in SQL Monitor, select the Send emails when alerts are raised check box:
If this check box is cleared, SQL Monitor will not send any emails, regardless of all other settings.
Setting up the default email address
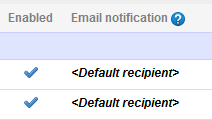
Enter an email address that all SQL Monitor emails will be sent to by default in the Send emails to box. This is the email address that will be shown on the Alert settings page as the <Default recipient>:
To add multiple email addresses, separate each with a comma. You can later customize the email recipient for different alert types or servers. If you subsequently change the email address in the Send emails to box, this will be automatically applied to any alerts that use <Default recipient>. Alerts where you have specified a different email recipient will not be affected.
Entering a send from email address
The Send from email address is the email address that will appear in the From field for all email messages sent by SQL Monitor when an alert is raised.
Enter the email address in the format: username@domain.com. You can only send a test email when a valid address in the right format has been entered. You can enter the Send emails to and Send from addresses before supplying your mail server details, but you won't be able to send the test email until your mail server details are provided. See Enter your mail server settings below.
Also send emails when
These are global options that apply to alerts that are raised with a status of Active.
Some types of alerts have a status of Event - their level cannot increase, and their status does not change to ended, so these options do not apply. For more information, see List of alerts.
An alert level increases
Some alerts can be configured with multiple thresholds: Low, Medium and High. These alerts are raised with a status of Active and can escalate automatically to a higher level when another threshold is passed. Select An alert level increases to specify that if this happens, a subsequent email should be sent.
No emails will be sent if:
- the level of an Active alert is automatically downgraded (for example, drops from High to Medium)
- an Active alert is downgraded and then subsequently escalates to its previous higher level
An alert's status changes to Ended
Active alerts automatically change to Ended when the condition that triggered them no longer applies; for example if memory used falls below the defined threshold for the alert, or if a backup is performed. Select An alert's status changes to Ended to specify that an email should be sent to inform the recipient that this particular occurrence of the alert has ended.
About PagerDuty
PagerDuty is an alarm aggregation and dispatching service. It collects alerts from your monitoring tools in a single repository, and notifies users via SMS, phone calls or emails. It enables to you to add alert severity filters, on-call scheduling, escalation policies and incident tracking to SQL Monitor.
How do I integrate SQL Monitor with PagerDuty?
There are integration guidelines in PagerDuty's Red Gate SQL Monitor Integration Guide. The only configuration change required in SQL Monitor is to add the PagerDuty integration email address to the Send emails to section of the Configuration >Email settings page.
Once you have created a SQL Monitor service in PagerDuty, you can edit the service settings. By default, PagerDuty will notify users of alerts with a status of high or medium, and low status alerts will be ignored. You can choose to be notified of all alerts, or high status alerts only.
Enter your mail server settings
If you don't know the DNS name or the IP address and port number of your outgoing SMTP mail server, check with your system administrator and enter them in the relevant text boxes.
Select Require a secure (SSL or TLS) connection to enable explicit SSL email. Once the SMTP connection is established, SSL is requested and the message delivered using the supplied credentials.
Also check with your administrator to find out whether your mail server requires a user name and password. If this is the case, select the Mail server requires a user name and password check box and enter details.
URL settings
When SQL Monitor sends an email notification, it includes a hyperlink to the alert. This hyperlink contains the name of your website. In some situations, this link will not work for other people (for example if the URL is localhost:<portnumber> this will only open SQL Monitor on your local computer).
If this is the case, you can enter the fully qualified URL to be included in the email hyperlink. Enter the URL in the Fully qualified website URL box.