Configuring Profiler trace
Published 08 July 2015
Enabling trace allows you to continuously capture SQL Profiler trace data on the selected instance. When an alert is raised, the SQL statements that were executing around the time of the alert are displayed under SQL Processes in the Performance data section for that alert.
Configuring trace
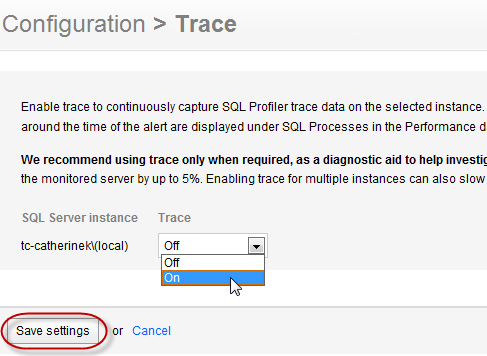
- Go to the Configuration tab. Under Monitoring, select Trace:
- For each SQL Server instance you want to store trace data for, Select On from the Trace drop-down list, then click the Save settings button.
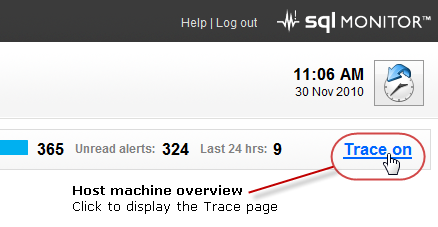
Warning icons are displayed to make it easier to see which instances on the page have trace enabled:The trace status is also displayed on the Host machine overview page:
What trace data is captured?
The following trace information is captured (SQL Server event number in brackets):
- RPC_Starting (11)
- SQL_BatchStarting (13)
- Audit_Login (14)
- Attention (16)
- SQL_Exception (33)
Storing and purging trace data
If trace is enabled, a trace data file is stored locally on the monitored server. Sections of the data file from around the time an alert was raised are copied to the SQL Monitor Data Repository. When you click on an alert in the Alert Inbox to display more details, the trace data is retrieved from the Data Repository.
Note: To prevent the trace data file from taking up excessive storage space on the monitored server, it is automatically deleted after it has remained on the server for 15 minutes, or reaches 1 GB in size.
Trace data stored in the Data Repository is categorized as SQL Server data for the purposes of purging. To specify how long to keep stored trace data in the Data Repository, use the SQL Server data purging option on the Data purging page (Configuration > Data purging).Trace data stored in the Data Repository is categorized as SQL Server data for the purposes of purging. To specify how long to keep stored trace data in the Data Repository, use the SQL Server data purging option on the Data purging page (Configuration > Data purging).