Versioning and Patching
Published 16 April 2018
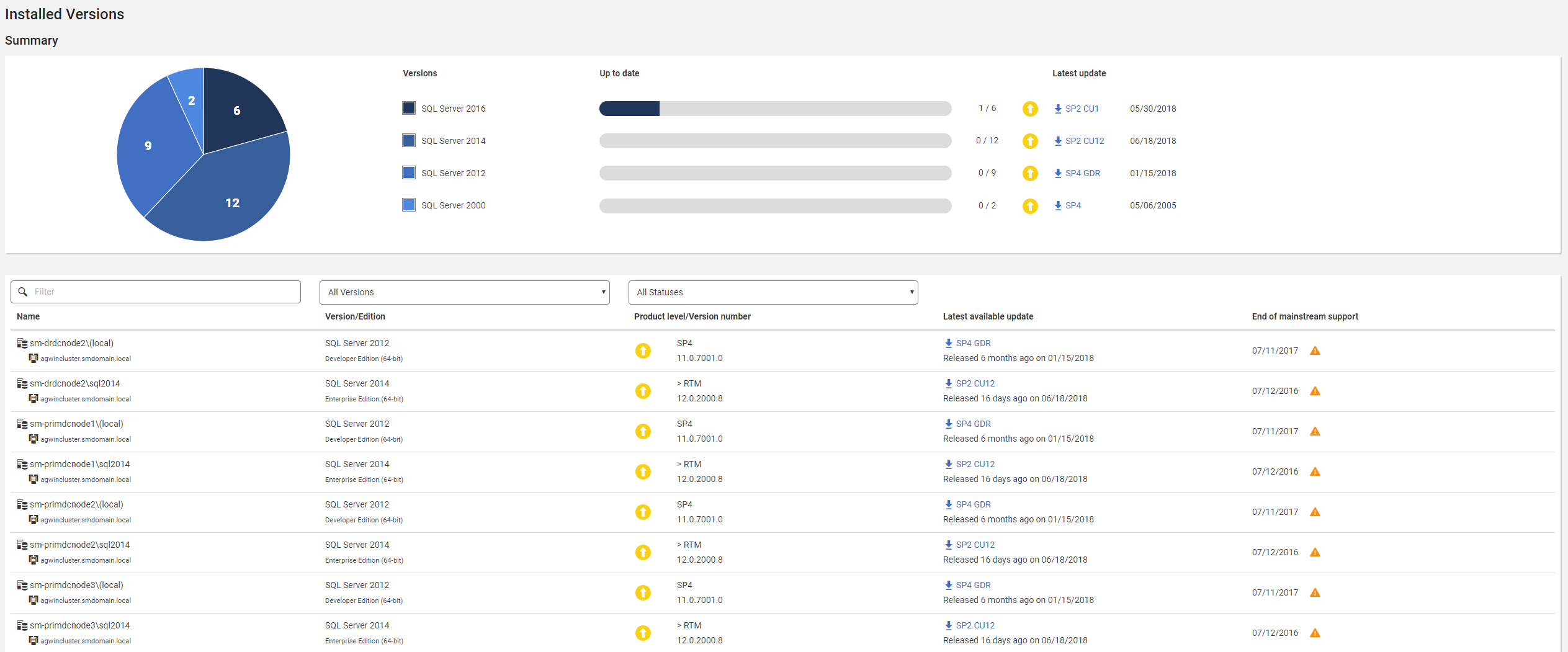
The Installed Versions page shows details of the versions of SQL Server installed across your monitored estate.
Understanding the Installed Versions page
The screenshot below shows an example of the data displayed on this page.
| Column Name | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Lists the monitored SQL instances, along with the machine that they are on and any relevant cluster information. | ||||
| Version/Edition | Shows the Specific SQL Server version and edition. | ||||
| Product level/Version number | Shows the service pack/cumulative update level and version number of the SQL instance. If the product level is preceded by a > (e.g. > RTM), it means that hotfixes or patches have been installed above the standard service pack or cumulative update levels The icon indicates whether the SQL instance is up to date with all available service packs/cumulative updates:
| ||||
Latest available update | Shows the latest available update for the installed version, and the date it was release. Clicking on the link will go to the download page for the update. This column will be blank if the installed version is the latest available. | ||||
| End of mainstream support | Shows the date when mainstream support from Microsoft for the installed version ends. will be shown if mainstream support has ended. |
Versions data
The versions data used by this page is obtained from the Redgate website and automatically updated each day. We aim to keep this up to date with the latest releases of SQL Server (for all versions that SQL Monitor supports).
If SQL Monitor cannot download updates to this data automatically, it can be performed manually. To do this, download the latest version of the data from https://www.red-gate.com/products/dba/sql-monitor/assets/sql-server-versions.json and save it to a file at C:\ProgramData\Red Gate\SQL Monitor\SqlServerVersions.json. SQL Monitor will then pick up the updated data from this file within 6 hours.