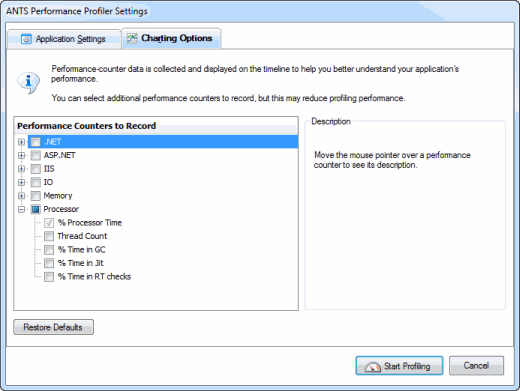
Setting up Charting Options
Published 03 December 2012
ANTS Performance Profiler can monitor the values of a number of built-in Windows performance counters while the application you are profiling is executing. The values of these counters are constantly updated on the timeline as profiling proceeds.
You choose the performance counters you want to monitor using the Charting Options tab on the ANTS Performance Profiler Settings dialog box.
Note that this feature requires ANTS Performance Profiler Professional.
Not all performance counters are appropriate to all application types that you may be profiling. You can find more information about individual performance counters under the Description group box, including details about a counter's relevance to particular application types.
Your choice will depend on your own requirements but, as an example, you might choose the following:
From the .NET group:
- The Gen 0 Promoted Bytes/sec counter
This will give the rate at which the garbage collector promotes objects from Generation 0 to Generation 1.
From the Memory group:
- The Working Set counter
This shows the total amount of physical memory used by your service (including memory used by shared DLLs and the .NET runtime itself)
From the Processor group
- The % Processor Time counter (selected by default)
This shows the percentage of time which all running threads use on the CPU. - The % Time in GC counter
This shows the percentage of time which the process was suspended to allow the last garbage collection to take place.
We recommend you avoid adding more performance counters than you need, as each additional counter that is recorded adds to the overhead introduced by the profiler. Adding too many counters may slow your application substantially.
Adding custom performance counters
You can add custom performance counters to the list of available counters in the Charting Options tab. To do this:
- Close ANTS Performance Profiler.
- Expose your performance counter to the Windows Performance Counter API using the PerformanceCounter andPerformanceCounterCategory classes of the System.Diagnostics namespace. (An example describing how to do this is given at http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.diagnostics.performancecounter.aspx)
Create a new XML file as follows:
<Counters> <Category Name="CategoryName"> <Counter Category="CategoryName" Name="CounterName" Units="Measurement Units"> <Instanced /> </Counter> </Category> </Counters>Ensure that CategoryName and CounterName are the same as the names used for the PerformanceCounterCategoryand PerformanceCounter. Remove the
<Instanced />node if your counter collects data about the computer, not only the individual process. You can add multiple categories and counters in the same XML file.- Save the XML file as UserCounters.xml in %LOCALAPPDATA%\Red Gate\ANTS Performance Profiler 7\.
- Restart ANTS Performance Profiler.
- The counters that you defined are shown in the list on the Charting Options tab.