Adding MySQL on Linux
Published 18 February 2025
Additional configuration required
Make sure you have prepared MySQL for monitoring before adding a MySQL instance to Redgate Monitor.
This page explains how to add MySQL instances running on self managed Linux.
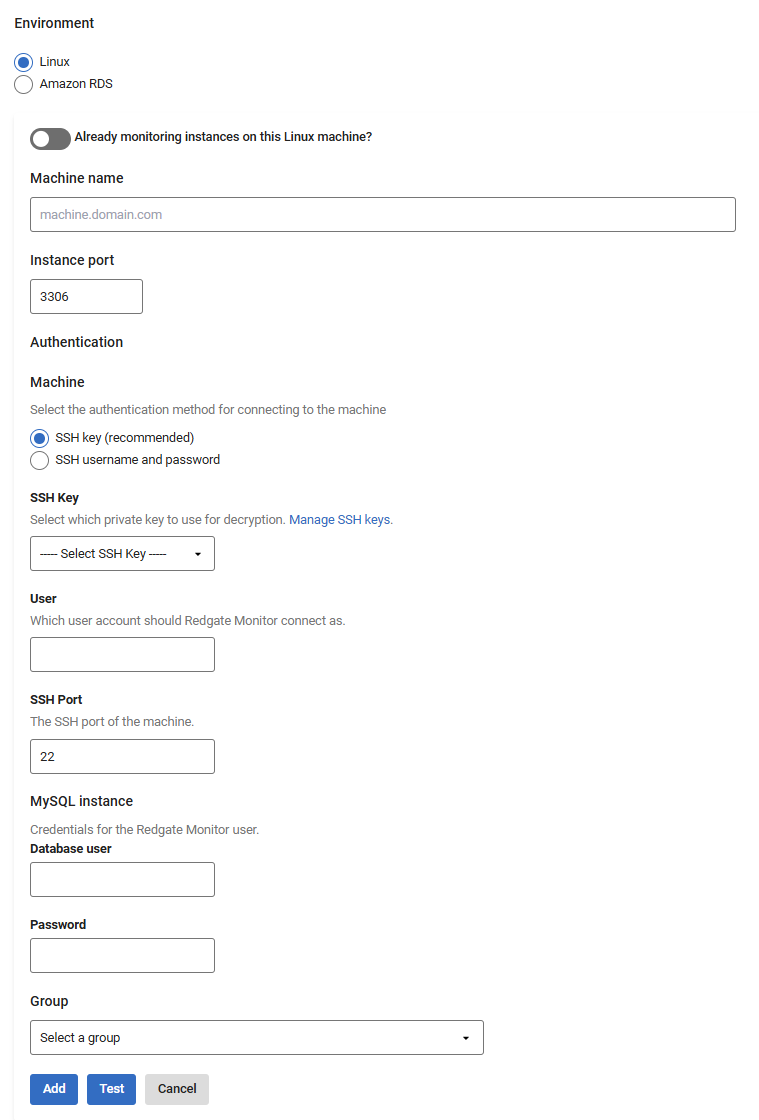
Go to Configuration → Monitored servers → Add → MySQL instance
To add the MySQL instance on a Linux machine, enter the machine IP address, under the machine name.
- You will need to provide two sets of credentials to connect to:
- The host Linux machine on which the instance is running.
- The MySQL instance.
Redgate Monitor uses SSH to connect to a Linux host, you can either use password authentication or public key authentication, see Connecting to a Linux Machine. For the instance, enter the MySql credentials.
Redgate Monitor does not require any root privileges for the SSH connection.
When you click Add, Redgate Monitor attempts to add the host machine and instance to the list of monitored servers:
Once added, the server name can't be edited. If you typed the name incorrectly, the server will be added with a status of "Connection failed (Unreachable)". To fix this, remove the server and add it again.Once a connection is established and a data collection event succeeded, the status is displayed as Monitoring (Connected). If Redgate Monitor encounters a problem and displays a different status, see Monitoring status explained.
Editing the credentials or properties of monitored servers
See Managing Monitored Servers.