Preparing MySQL for monitoring
Published 18 February 2025
Setting up a MySQL User
In the following commands replace:
- <password> with the password for the user being created
CREATE USER 'redgatemonitor'@'<host>' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>'; GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO redgatemonitor; GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO redgatemonitor; GRANT CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES ON *.* TO redgatemonitor;
CREATE USER 'redgatemonitor'@'<host>' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>'; GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO 'redgatemonitor'@'<host>'; GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO 'redgatemonitor'@'<host>' WITH GRANT OPTION; GRANT CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES ON *.* TO 'redgatemonitor'@'<host>';
If you would like to use MySql authentication (username and password):
CREATE USER 'redgatemonitor'@'<host>' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>';
If you would like to use Microsoft Entra Managed Identity or Microsoft Entra Service Principal authentication:
CREATE AADUSER 'redgatemonitor' IDENTIFIED BY '<Application/Client ID>';
Once the user has been created, you will need to assign the appropriate permissions:
GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO redgatemonitor; GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO redgatemonitor; GRANT CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES ON *.* TO redgatemonitor;
Configuring MySQL Instances
You will need to connect to the MySQL instance and create a database which Redgate Monitor can use to create temporary tables within:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS redgatemonitor_db;
Configuring MySQL Instances to track statement execution CPU time
Make sure that events_statements_cpu is enabled by running following command
SELECT * FROM performance_schema.setup_consumers WHERE NAME LIKE '%statements%';
If the ENABLED column is set to NO, please run the following:
UPDATE performance_schema.setup_consumers SET ENABLED = 'YES' WHERE NAME = 'events_statements_cpu';
By default, performance_schema is disabled in Amazon RDS for MySQL and Amazon Aurora MySQL.
You will need to enable it by modifying your RDS/Aurora parameter group, as csystem variables in RDS/Aurora cannot be directly changed with SET statements.
Step 1: Create a Custom Parameter Group
Amazon Aurora and RDS do not allow modifying performance_schema directly on the instance, so you must create a custom DB parameter group.
- Sign in to AWS Management Console and go to Aurora and RDS.
- In the left menu, click Parameter groups.
- Click Create parameter group.
- Choose:
- Parameter group family: Select the correct MySQL version (e.g.,
mysql8.0). - Type: Select DB Parameter Group.
- Name: Enter a descriptive name, e.g.,
mysql-custom-params. - Description: (Optional) Add a description.
- Parameter group family: Select the correct MySQL version (e.g.,
- Click Create.
Step 2: Modify the Parameter Group
- Find your newly created DB parameter group and click on it.
- Search for
performance_schema. - Change its value from 0 to 1.
- Click Save changes.
Step 3: Apply the Custom Parameter Group to Your Aurora or RDS Instance
- Go to Aurora and RDS → Databases.
- Select your MySQL RDS instance or MySQL Aurora instance.
- Click Modify.
- Scroll down to DB parameter group and select the custom parameter group you created.
- Click Continue.
- Select Apply Immediately (or apply it during the next maintenance window).
- Click Modify DB Instance.
Step 4: Reboot the Aurora or RDS Instance
The changes won’t take effect until you reboot:
- Go to Aurora and RDS → Databases.
- Select your MySQL instance.
- Click Actions → Reboot.
- Confirm the reboot.
Step 5: Enable events_statement_cpu
- Connect to your MySQL instance with a user that has UPDATE permissions on the performance_schema
- Run
UPDATE performance_schema.setup_consumers SET ENABLED = 'YES' WHERE NAME = 'events_statements_cpu';
Please note that the UPDATE performance_schema query must be executed each time the MySQL instance is restarted as changes to performance_schema via queries do not persist across restarts.
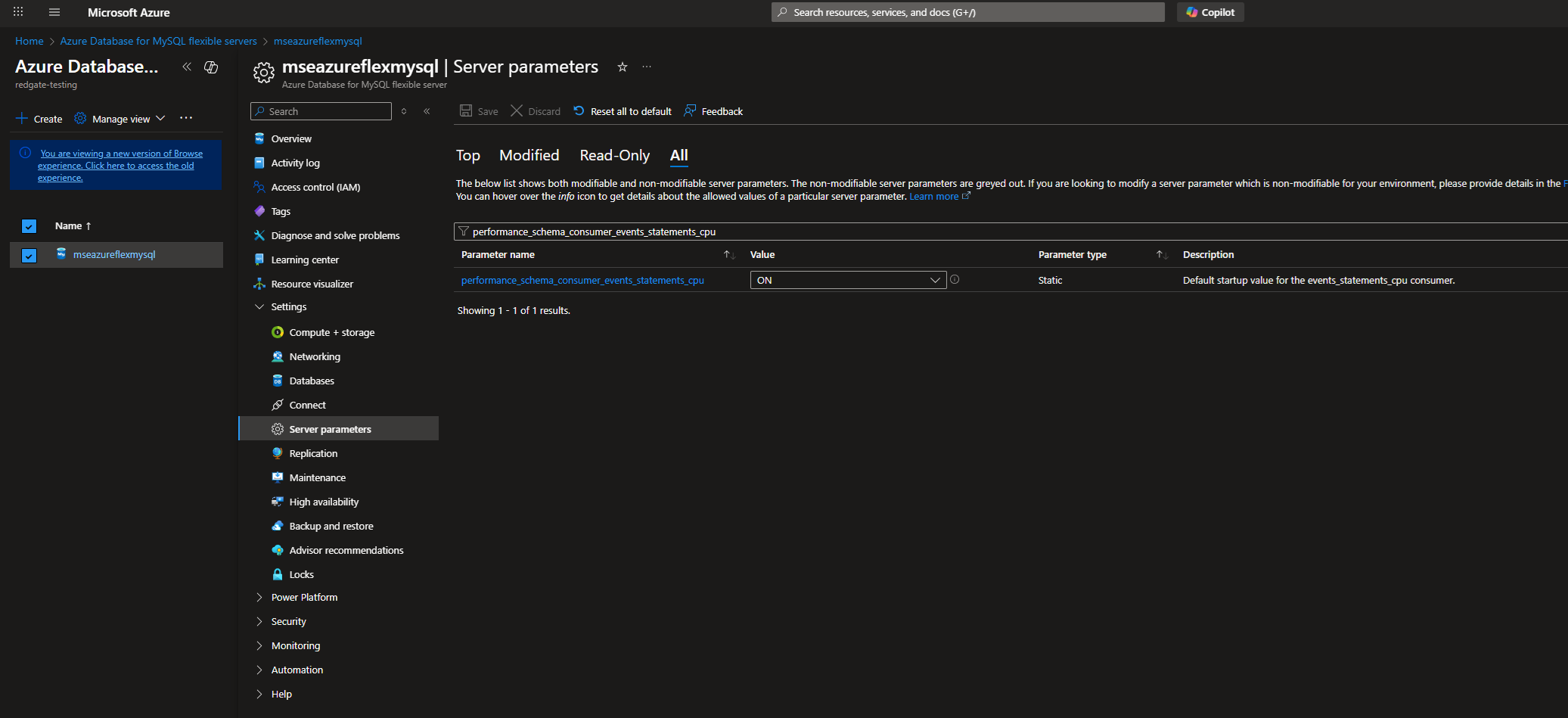
Go to your Azure portal and locate your Azure Flex for MySql instance. Navigate to Settings > Server Parameters > All and then search for 'performance_schema_consumer_events_statements_cpu'
If the VALUE column is set to OFF, please flip the switch to ON.
Configuring query text length
By default, MySQL truncates query text stored in the Performance Schema to 1024 characters. This limit is controlled by the performance_schema_max_sql_text_length system variable. If your queries exceed this length, Redgate Monitor will only display the truncated portion.
To increase this limit, add the following to your MySQL configuration file (my.cnf or my.ini) and restart the MySQL server:
[mysqld] performance_schema_max_sql_text_length = 4096
Note: increasing this value will use more memory in the Performance Schema.