Switches used in the command line
Published 21 August 2019
This is a list of switches you can use with the SQL Compare command line.
- The first data source ( /db1, /b1, etc) is the source.
- The second data source ( /db2, /b2, etc) is the target.
/AbortOnWarnings:<warning level>
Alias: /aow
Specifies that SQL Compare won't run a deployment if there are any serious deployment warnings. If you don't specify this switch, SQL Compare will ignore warnings and run the deployment.
Arguments
| None | Don't abort on warnings |
| Medium | Abort on medium or high warnings |
| High | Abort on high warnings |
The default is None. If you set this switch to Medium or High and there are deployment warnings, then exit code 61 will be returned.
For more information on warnings in SQL Compare, see Deployment Warnings.
/activateSerial:<serial number>
- This switch is case sensitive.
- An internet connection is required to activate SQL Compare from the command line.
For information about how to activate manually without an internet connection, see Activating.
You can specify a SQL Compare Professional serial number, or a serial number for bundle such as the SQL Toolbelt Essentials:
sqlcompare /activateSerial:123-456-789012-ABCD
If you're using the SQL Compare command line on a server, you need to use the /allUser switch in addition to /activeSerial. Learn more about Using the command line on a service account in Windows.
/allUsers
Activates SQL Compare command line for all users (including Windows service accounts). For more information see: Using the command line on a service account in Windows
/activedirectory1
Alias: /ad1
Uses Azure active directory authentication with the first database. If a username and password combination is specified, then Active Directory password authentication will be used.
/activedirectory2
Alias: /ad2
Uses Azure active directory authentication with the second database. If a username and password combination is specified, then Active Directory password authentication will be used.
/Argfile:<file path>
Runs a file containing an XML argument specification:
sqlcompare /Argfile:XMLFileName.xml
For more information, see Using XML to specify command line arguments.
/Assertidentical
When /assertidentical is specified, SQL Compare will return an exit code of 0 if the objects being compared are identical. If they aren't identical, it will return exit code 79.
/Backup1:<file path1>;<file path2>;...;<file pathN>
Alias: /b1
Specifies the backup to be used as the source. You must add all of the files making up the backup set you want to compare:
sqlcompare /Backup1:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetStaging.bak /db2:WidgetStaging
To specify more than one backup file, the file names are separated using semicolons:
sqlcompare /Backup1:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetDev_Full.bak; D:\BACKUPS\WidgetDev_Diff.bak /db2:WidgetDev
For more information, see Working with backups.
/Backup2:<file path1>;<file path2>;...;<file pathN>
Alias: /b2
Specifies the backup to be used as the target. You must add all of the files making up the backup set you want to compare:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /Backup2:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetStaging.bak
/BackupCompression:<compression level>
Alias: /bc
Compresses a backup using one of three compression levels.
Arguments
| 1 | Compression level 1 is the fastest compression, but results in larger backup files. On average, the backup process is 10% to 20% faster than when compression level 2 is used, and 20% to 33% fewer CPU cycles are used. Backup files are usually 5% to 9% larger than those produced by compression level 2. However, if a database contains frequently repeated values, compression level 1 can produce backup files that are smaller than if you used compression level 2 or 3. For example, this may occur for a database that contains the results of Microsoft SQL Profiler trace sessions. |
| 2 | This compression level uses the zlib compression algorithm, and is a variation of compression level 3. On average, the backup process is 15% to 25% faster than when compression level 3 is used, and 12% to 14% fewer CPU cycles are used. Backup files are usually 4% to 6% larger. |
| 3 | Compression level 3 uses the zlib compression algorithm. This compression level generates the smallest backup files in most cases, but it uses the most CPU cycles and takes the longest to complete. |
You can only compress Redgate (SQL Backup Pro) backups.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupcompression:3
/BackupEncryption
Alias: /be
Encrypts a backup using 128-bit encryption.
- You can only encrypt Redgate (SQL Backup Pro) backups.
- If you encrypt a backup, you must specify a password using /BackupPassword.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupencryption /backuppassword:P@ssw0rd
/BackupFile:<file name>
Alias: /bf
The file name to use when creating a backup.
For Redgate backups, use the file extension .sqb. For native SQL Server backups, use .bak.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupfile:WidgetProductionBackup.sqb
/BackupFolder:<folder path>
Alias: /bd
The folder to use for storing backups.
If you don't use this switch, backups are stored in the folder specified in the SQL Backup options for the SQL Server instance. If you're not using SQL Backup, or no backup file locations have been set up, backups are stored in the SQL Server instance's default backup folder, for example:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.SQL2012\MSSQL\Backup
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupfolder:C:\Backups
/BackupNumberOfThreads:<number of threads>
Alias: /bth
Uses multiple threads to speed up the backup process. SQL Backup can use up to a maximum of 32 threads.
We recommend you start with one thread fewer than the number of processors. For example, if you are using four processors, start with three threads.
You can only use multiple threads with Redgate (SQL Backup Pro) backups.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupnumberofthreads:2
/BackupOverwriteExisting
Alias: /boe
Overwrites existing backup files of the same name when creating a backup.
/BackupType:<backup type>
Alias: /bt
The type of backup to perform.
Arguments
| Full | Full backup |
| Differential | Differential backup |
The default is Full.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backuptype:differential
/BackupPassword:<password>
Alias: /bp
The password to use when encrypting a backup.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupencryption /backuppassword:P@ssw0rd
/BackupPasswords1:<password1>,<password2>,...,<passwordN>
Alias: /bpsw1
Specifies the password for the source backup.
sqlcompare /Backup1:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetStaging.bak /BackupPasswords1:P@ssw0rd /db2:WidgetProduction
/BackupPasswords2:<password1>,<password2>,...,<password1N>
Alias: /bpsw2
Specifies the password for the target backup.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /Backup2:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetProduction.bak /BackupPassword2:P@ssw0rd
Contents
/BackupProvider:<backup format>
Alias: /bpr
The format of the backup file to create when backing up the target database.
Arguments
Native | Native SQL Server backup (.bak) |
SQB | SQL Backup Pro backup (.sqb) |
The default is native in SQL Compare 11.1.5 and later. On previous versions, the default was SQB.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup /backupprovider:native
/BackupSet1:<backup set>
Alias: /bks1
If you are comparing a backup set that contains multiple files, use the /BackupSet1 switch to specify the files which make up the source backup set, and use the /BackupSet2 switches to specify the files which make up the target:
sqlcompare /Backup1:"D:\MSSQL\BACKUP\WidgetDev.bak" /BackupSet1:"2008-09-23 Full Backup" /db2:WidgetLive
If the backup set switches aren't specified, SQL Compare uses the latest backup set.
To specify more than one backup file, the file names are separated using semi-colons.
sqlcompare /Backup1:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetDev_Full.bak; "D:\BACKUPS\WidgetDev_Diff.bak" /db2:WidgetDevlopment
For encrypted backups that have been created using SQL Backup, use the /BackupPasswords1 and /BackupPasswords2 switches to specify the passwords; when there is more than one password, the passwords are separated using semi-colons.
sqlcompare /Backup1:D:\BACKUPS\WidgetDev.sqb /BackupPassword1:Pa$$w0rd /db2:WidgetLive
/BackupSet2:<backup set>
Alias: /bks2
Specifies which backup set to use for the target backup:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetProduction /BackupSet2:"2008-09-23 Full Backup"
/Database1:<database name>
Alias: /db1
Specifies a database to use as the source:
sqlcompare /Database1:WidgetStaging /Database2:WidgetProduction
/Database2:<database name>
Alias: /db2
Specifies a database to use as the target.
/DataCompareOptions:<option1>,<option2>,<option3>
Alias: /dco
Applies the project configuration options used during comparison or deployment of static data:
sqlcompare /script1:"C:\Scripts Folders\Widget staging scripts\" /db2:WidgetProduction /Include:StaticData /DataCompareOptions:Default,DropConstraintsAndIndexes
This uses the data compare options found in SQL Data Compare Options with the exception of the default options which are:
IgnoreSpaces, IncludeIdentities, DisableKeys, OutputCommentHeader, ReseedIdentity, MissingFrom2AsInclude
/deactivateSerial
Attempts to deactivate the application. An internet connection is required to deactivate the product.
/empty2
Use this as the target data source to make a script that creates the source database schema. You can use this script with SQL Packager 8.
For example, you want to package the schema of a database, WidgetStaging, so that when the package is run it will create a copy of the database schema.
sqlcompare /Server1:MyServer\SQL2014 /Database1:WidgetStaging /empty2 /ScriptFile:"C:\Scripts\WidgetStagingSchema.sql"
/exclude:<type>:<regular expression>
Excludes objects from the comparison. For example, to exclude objects that are identical in both the source and target:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /exclude:Identical
To exclude an object type:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /exclude:table
To exclude specific objects, use a regular expression:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /exclude:table:Widget*
For more examples using regular expressions, see Selecting tables with unrelated names.
If you want to set up complex rules to exclude objects (eg to exclude tables with a specific name and owner), use a filter instead.
To exclude more than one object or object type, use multiple /exclude switches:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /exclude:table:WidgetReferences /exclude:view
- If an object is matched by both /include and /exclude, the /exclude rule takes priority and the object is excluded.
- You can't use /exclude with the /project switch.
<type> values
- Additional
Objects that aren't in the source (eg /db1). - Missing
Objects that aren't in the target (eg /db2). - Different
Objects that are the source and the target, but are different. - Identical
Objects that are identical in the source and the target. - Static data
Static data in a source-controlled database or a scripts folder.
To exclude object types, use:
- Assembly
- AsymmetricKey
- Certificate
- Contract
- DdlTrigger
- EventNotification
- ExtendedProperty
- ExternalDataSource
- ExternalFileFormat
- ExternalTable
- FullTextCatalog
- FullTextStoplist
- Function
- MessageType
- PartitionFunction
- PartitionScheme
- Queue
- Role
- Route
- Rule
- Schema
- SearchPropertyList
- Sequence
- Service
- ServiceBinding
- StoredProcedure
- SymmetricKey
- Synonym
- Table
- User
- UserDefinedType
- View
- XmlSchemaCollection
/Filter
Alias: /ftr
Specifies a custom filter to select objects for deployment.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /filter:MarketingViewsOnly.scpf
You can set up a filter to include or exclude objects based on their type, name, and owner (schema) name.
This is useful, for example, if you want to create complex selection rules without using regular expressions.
- Filters are set up in the user interface.
- Filters are saved with the extension .scpf
- /filter can't be used with /Include or /Exclude.
- If you use /filter with /project, the filter you specify overrides any filter used in the project.
For more information, see Using filters.
/Force
Alias: /f
Forces the overwriting of any output files that already exist. If this switch isn't used and a file of the same name already exists, the program will exit with the exit code indicating an IO error.
/Help
Alias: /?
Displays the list of switches in the command line with basic descriptions.
If /help is used with any switches except /verbose, /html, /out, /force or /outputwidth then those extra switches will be ignored; the help message will be printed and the process will end with exit code 0.
/HTML
Outputs the help text as HTML. Must be used with the /help switch.
/IgnoreParserErrors
If SQL Compare encounters any high level errors when parsing a scripts folder, it will exit with an error code of 62.
Use /ignoreParserErrors to force SQL Compare to continue without exiting.
/IgnoreSourceCaseSensitivity
When you are creating a scripts folder using /makescripts, SQL Compare automatically detects the case sensitivity of the data source.
Use /ignoreSourceCaseSensitivity to disable automatic detection of case sensitivity.
/include:<type>:<regular expression>
Includes objects in the comparison. For example, to include tables:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /include:table
To include specific objects, use a regular expression:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /include:table:Widget*
For more examples using regular expressions, see Selecting tables with unrelated names.
If you want to set up complex rules to include objects (eg to include tables with a specific name and owner), use a filter instead.
To include more than one object or object type, use multiple /include switches:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /include:table:WidgetReferences /include:view
- If an object is matched by both /include and /exclude, the /exclude rule takes priority and the object is excluded.
- You can't use /include with the /project switch.
<type> values
- Additional
Objects that aren't in the source (eg /db1). - Missing
Objects that aren't in the target (eg /db2). - Different
Objects that are the source and the target, but are different. - Identical
Objects that are identical in the source and the target. - StaticData
Static data in a source-controlled database or a scripts folder. Can't be used with snapshot data sources. Note that this only includes the static data in the deployment script, not in e.g. generated reports.
To include object types, use:
- Assembly
- AsymmetricKey
- Certificate
- Contract
- DdlTrigger
- EventNotification
- ExtendedProperty
- ExternalDataSource
- ExternalFileFormat
- ExternalTable
- FullTextCatalog
- FullTextStoplist
- Function
- MessageType
- PartitionFunction
- PartitionScheme
- Queue
- Role
- Route
- Rule
- Schema
- SearchPropertyList
- Sequence
- Service
- ServiceBinding
- StoredProcedure
- SymmetricKey
- Synonym
- Table
- User
- UserDefinedType
- View
- XmlSchemaCollection
/LogLevel:<level>
Alias: /log
Creates a log file with a specified minimum log level.
Log files collect information about the application while you are using it. These files are useful to us if you have encountered a problem. For more information, see Logging and log files.
Arguments
None | Disables logging |
Error | Reports serious and fatal errors |
Warning | Reports warning and error messages |
Verbose | Reports all messages in the log file |
The default is None.
For example:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /makeScripts:"D:\ScriptsFolder" /logLevel:Verbose
/MakeBackup
Backs up the target database using Redgate SQL Backup Pro or SQL Server native.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /sync /makebackup
/MakeScripts:<folder>
Alias: /mkscr
Creates a scripts folder from the data source.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /makeScripts:"C:\Scripts Folders\Widget staging scripts"
If the folder already exists an error will occur. To merge scripts into an existing scripts folder, compare them with that folder and use the /synchronize switch:
sqlcompare /scr1:"C:\Scripts Folders\Widget dev scripts" /scr2:"C:\Scripts Folders\Widget staging scripts" /synchronize
For more information, see Working with scripts folders.
/MakeSnapshot:<file name>
Alias: /mksnap
Creates a snapshot from the data source.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /makeSnapshot:"C:\Widget Snapshots\StagingSnapshot.snp"
If the file already exists an error will occur, unless you have also used the /force switch.
/Options:<option1>,<option2>,<option3>
Alias: /o
Applies the project configuration options used during comparison or deployment:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /options:Default,IgnoreWhiteSpace
For a detailed list of these options see Options used in the command line.
/Out:<file path>Redirects console output to the specified file:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /out:C:\output file
/OutputProject:<file path>
Alias: /outpr
Writes the settings used for the comparison to the specified SQL Compare project file:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /options:Default,IgnoreWhiteSpace /outputProject:"C:\WidgetProject.scp"
This also generates a SQL Compare project file. These files end with a .scp extension. If the file already exists an error will occur, unless you have also used the /force switch.
/OutputWidth:<columns>
Forces the width of console output.
This can be used to ensure that database object names etc aren't truncated, and that SQL script lines aren't wrapped or broken. This is particularly useful when redirecting output to a file as it allows you to overcome the limitations of the default console width of 80 characters.
/Password1:<password>
Alias: /p1
The password for the source database.
You must also provide a username. If you don't specify a username and password combination, integrated security is used:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /userName1:User1 /password1:P@ssw0rd /db2:WidgetProduction /userName2:User2 /password2:Pa$$w0rd
/Password2:<password>
Alias: /p2
The password for the target database.
/Project:<file path>
Alias: /pr
Uses a SQL Compare project (.scp) file for the comparison.
To use a project you have saved as "widgets.scp" from the command line:
sqlcompare /project:"C:\SQLCompare\Projects\Widgets.scp"
- When you use a project, all objects will be selected rather than only those that were selected for comparison when you saved the project.
- You can't use the /include and /exclude switches with /project unfortunately.
- Use /options to specify any additional options you want to use with a command line project. For more information, see Options used in the command line.
- It is possible to override the target data source specified in the project by using, for example, the /Server2 and /Database2 switches in addition to the /Project switch.
The /project switch is useful, for example, as you can't specify a custom filter in the command line.
For more information on using projects, and what a project contains, see Working with projects.
/Quiet
Alias: /q
Quiet mode: no output.
/Report:<file path>
Alias: /r
Generates a report and writes it to the specified file.
The type of report is defined by the /reportType switch. If the file already exists an error will occur, unless you have used the /force switch:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /report:"C:\reports\WidgetReport.html" /reportType:Excel
Supported extensions are: html, htm, xml and xls.
/ReportAllObjectsWithDifferences
Alias: /rad
Includes all objects with differences in the reports, rather than all selected objects.
/ReportType:<report type>
Alias: /rt
Supported values
XML | Simple XML report |
| Html | Interactive HTML report |
Classic | Classic HTML report (displays differences side by side) |
Excel | Microsoft Excel spreadsheet |
The classic HTML report type is not able to be generated with the linux commandline.
This switch defines the file format of the report produced by the /Report switch.
For example:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /report:"C:\reports\WidgetReport.html" /reportType:Html
If this switch is omitted, the default setting is XML. However, in version 13.1 an additional attempt is made to automatically infer the report type from the file name extension of the report file specified using the /Report switch. Supported extensions are: html, htm, xml and xls.
For more information, see Exporting the comparison results.
/Revision1:<revision>
Alias: /r1
Specifies the source control revision of the source database. To specify a revision, the database must be linked to SQL Source Control. To specify the latest version, type: HEAD
Specifying a revision other than HEAD is only supported with TFS, SVN and Vault. If you're using another source control system, we recommend checking the revision out to a local folder and using the /Scripts1 switch.
The following example compares revision 3 of WidgetStaging with the latest revision of WidgetProduction:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /revision1:3 /db2:WidgetProduction /revision2:HEAD
/Revision2:<revision>
Alias: /r2
Specifies the source control revision of the target database. To specify a revision, the database must be linked to SQL Source Control.
/Sca1:<file path>
Specifies the .sqlproj file for the SQL Change Automation project to use as the source.
sqlcompare /sca1:"C:\ScaProject\ScaProject.sqlproj" /db2:WidgetProduction
/Sca2:<file path>
Specifies the .sqlproj file for the SQL Change Automation project to use as the target.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetProduction /sca2:"C:\ScaProject\ScaProject.sqlproj"
/ScriptFile:<file path>
Alias: /sf
Generates a SQL script to migrate the changes which can be executed at a later time. If the file already exists an error will occur, unless you use the /force switch:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /scriptFile:"C:\Scripts Folder\WidgetSyncScript.sql"
/Scriptfile can be used when the target ( /db2, /scr2, /sn2 ) is a database, a snapshot, or a scripts folder.
If the target is a snapshot or a scripts folder, the generated script modifies a database with the schema represented by that snapshot or scripts folder.
/Scripts1:<folder>
Alias: /scr1
Specifies the scripts folder to use as the source:
sqlcompare /scripts1:"C:\Scripts Folder\WidgetStagingScript" /db2:WidgetProduction
/Scripts2:<folder>
Alias: /scr2
Specifies the scripts folder to use as the target.
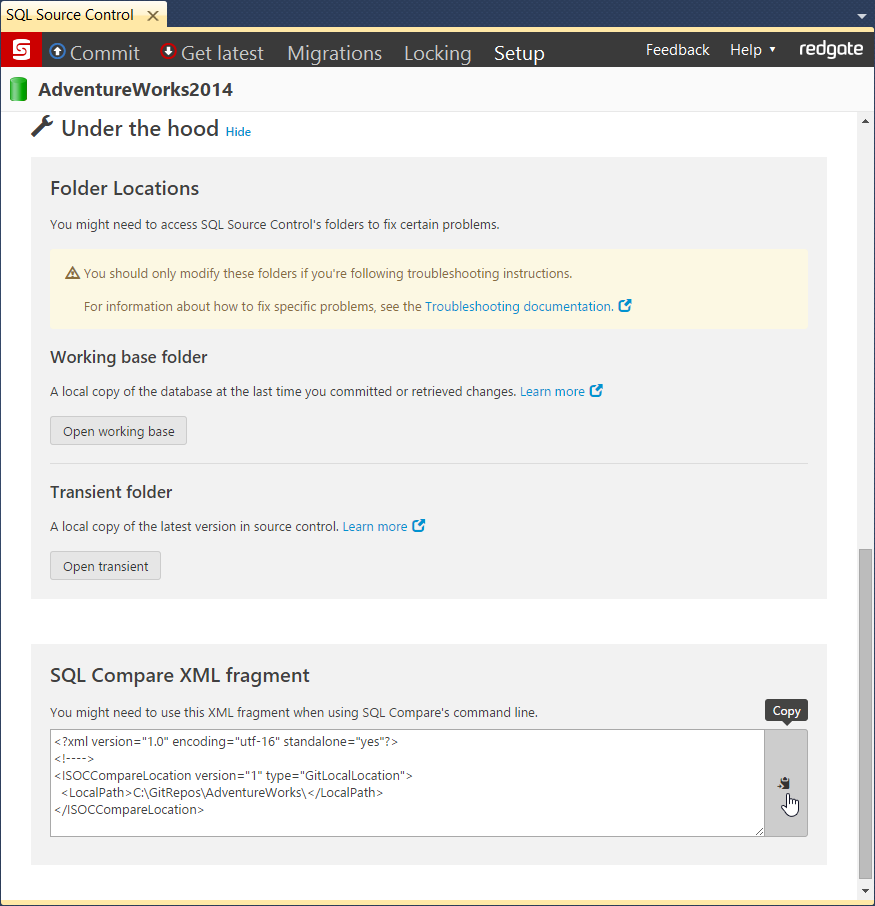
/ScriptsFolderXML:<file path>
Alias: /sfx
The path to a text file containing XML that describes the location of a source control repository.
- In the SQL Source Control Setup tab for a source-controlled database, click on the Show link next to Under the hood
- Copy the XML fragment from the SQL Compare XML fragment block to the clipboard by clicking the Copy button:
- Create a new text file and paste the XML fragment into it.
- Save the file.
/Server1:<server name>
Alias: /s1
Specifies the server on which the source (/db1:) database is located. If an explicit path isn't specified, it defaults to Local.
sqlcompare /server1:Widget_Server\SQL2008 /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction
A non-default port can be specified, as well as connecting with encrypt=true and trustservercertificate=true (when set to true, SSL is used to encrypt the channel when bypassing walking the certificate chain to validate trust.)
sqlcompare /server1:"Widget_Server\SQL2008,<port>;encrypt=true;trustservercertificate=true" /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction
When running on Linux
The backslash '\' is an escape character in bash. You should therefore specify the server as '/server1:Widget_Server\\SQL2008' when using the Linux commandline.
/Server2:<server name>
Alias: /s2
Specifies the server on which the target (/db2:) database is located. If an explicit path isn't specified, it defaults to Local.
/ShowWarnings
Alias: /warn
Displays any warnings that apply to the deployment. For more information on warnings in SQL Compare, see Warnings.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /showWarnings
/Snapshot1:<file name>
Alias: /sn1
Specifies the snapshot to use as the source:
sqlcompare /snapshot1:"C:\Snapshots\WidgetStagingSnapshot.snp" /db2:WidgetProduction
/Snapshot2:<file path>
Alias: /sn2
Specifies the snapshot to use as the target:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /snapshot2:"C:\Snapshots\WidgetProductionSnapshot.snp"
/Sourcecontrol1
Specifies a folder of source-controlled scripts to use as the source.
If you use this switch, you must also specify /scriptsfolderxml.
If you want to use a specific revision of the database, you can also specify /revision1.
sqlcompare /sourcecontrol1 /revision1:100 /sfx:"C:\Files\scripts.txt" /db2:WidgetProduction
/Sourcecontrol2
Specifies a folder of source-controlled scripts to use as the target.
If you use this switch, you must also specify /scriptsfolderxml.
If you want to use a specific revision of the database, you can also specify /revision2.
sqlcompare db1:WidgetStaging /sourcecontrol2 /revision2:100 /sfx:"C:\Files\scripts.txt"
/Synchronize
Aliases: /sync or /synchronise
Synchronizes (deploys) the databases after comparison.
The target (for example, /db2) is modified; the source (for example, /db1) isn't modified:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /synchronize
/SyncScriptEncoding:<script encoding>
Alias: /senc
Arguments
UTF8 | UTF-8 encoding, without preamble |
UTF8WithPreamble | UTF-8 encoding, with 3-byte preamble |
Unicode | UTF-16 encoding |
ASCII | ASCII encoding |
Used with /scriptFile. Specifies the character encoding used when writing the SQL script file. The default is UTF8.
For example:
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /db2:WidgetProduction /scriptFile:"C:\Scripts Folder\WidgetSyncScript.sql" /syncScriptEncoding:ASCII
/TransactionIsolationLevel:<transaction isolation level>
Alias: /til
Specifies the transaction isolation level to set in the deployment script. For information about transaction isolation levels, see SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL (MSDN).
Arguments
| READ UNCOMMITTED |
| READ COMMITTED |
| REPEATABLE READ |
| SNAPSHOT |
| SERIALIZABLE |
/UserName1:<username>
Alias: /u1
The username for the source database.
If no username is specified, integrated security is used.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /userName1:User1 /password1:P@ssw0rd /db2:WidgetProduction /userName2:User2 /password2:Pa$$w0rd
/UserName2:<username>
Alias: /u2
The username for the target database.
If no username is specified, integrated security is used.
/Verbose
Alias: /v
Verbose mode.
/VersionUserName1:<username>
Alias: /vu1
Specifies the username for the source control server linked to the source database.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /v1:3 /versionUserName1:User1 /vp1:P@ssw0rd /db2:WidgetProduction /v2:HEAD /versionUserName2:User2 /vp2:Pa$$w0rd
If you have a username saved in SQL Source Control, you don't need to specify it in the command line.
/VersionUserName2:<username>
Alias: /vu2
Specifies the username for the source control server linked to the target database.
/VersionPassword1:<password>
Alias: /vp1
Specifies the password for the source control server linked to the source database.
sqlcompare /db1:WidgetStaging /v1:3 /vu1:User1 /versionpassword1:P@ssw0rd /db2:WidgetProduction /v2:HEAD /vu2:User2 /versionpassword2:Pa$$w0rd
If you have a password saved in SQL Source Control, you don't need to specify it in the command line.
/VersionPassword2:<password>
Alias: /vp2
Specifies the password for the source control server linked to the target database.
Deprecated options
/AllowIdenticalDatabases
This switch is deprecated. Instead use /include:Identical
/include:Identical suppresses the exit code if the two data sources are identical.
If /include:Identical isn't set, and the data sources are identical, SQL Compare returns the error code 63.
/IncludeIdentical:<IncludeIdentical>
This switch is deprecated. Instead use /include:Identical.