Working with custom metrics and alerts
Published 03 December 2012
What is a custom metric?
By default, SQL Monitor collects a standard set of Machine, SQL Server and Database metrics from every monitored object. It does so by running a T-SQL query against the objects at regular intervals and displaying the collected values as data points on the Analysis page.
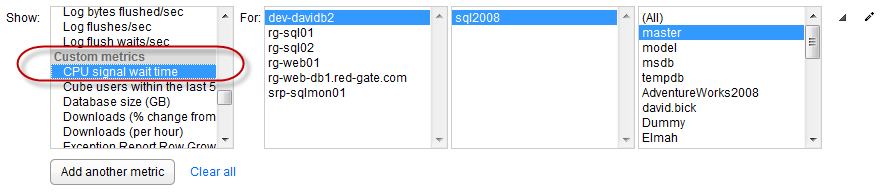
Custom metrics are different; you add your own T-SQL query, choose the instances and databases to collect from, and specify the frequency of collection. This means data unique to your server environment can be collected and analyzed. Each time the query runs, a single, numeric value is collected. Values are displayed as data points on the Analysis page when you select a custom metric from the Show drop-down list:
What is a custom alert?
A custom alert warns you when a custom metric value passes a specified threshold for a certain duration. Adding a custom alert is optional, but it is a useful way of finding out if the values collected by a custom metric suggest problems with your databases.
Custom alerts are Continuous alerts that are raised at a defined level (Low, Medium or High). They can have the following status:
- Active: the issue that triggered the alert is still a problem
- Ended: the issue has been resolved
You can configure multiple thresholds so that if the collected metric value changes, the Active alert will automatically escalate or downgrade from the threshold level at which it was raised.
Once created, the custom alert behaves just like the alerts provided by default and displayed in the Alert Inbox or the Alert settings page (Configuration > Alert settings).
How do I create a custom metric and alert?
A simple wizard guides you through each step of the creation process. See Creating custom metrics and alerts.
If you don't want to create a custom metric and alert from scratch, we've provided a website, SQL Monitor Metrics, containing a range of metrics that you can install these metrics automatically.
Automatic metric installation is only available in SQL Monitor 3.2 and later.