Hardware and performance guidelines
Published 08 March 2018
For the purposes of this page, a server is defined as a host machine plus a single SQL Server instance.
These values are guidelines only. They are based on our experience of typical server workload and the typical performance of the system that SQL Monitor is running on. If you are monitoring host machines with several instances and highly-active databases, you may require more performant hardware, and if you are monitoring relatively quiet servers you may require less.
Key performance requirements
A SQL Monitor installation has three components:
- a number of base monitors, responsible for sampling, managing and interpreting the sampled data,
- the repository, a SQL Server database that holds the sampled data and SQL Monitor configuration settings,
- one web server sitting between users and the data sampled by the base monitor.
Base monitor capabilities
We recommend that each base monitor supports a maximum of 250 servers.
Requirements change with server load. For instance, monitoring 500 servers with a single instance requires fewer resources than monitoring 200 servers each running 100 instances with many concurrent connections.
Web server requirements
The specification of the web server depends on how many people will access it and from where. We recommend allowing plenty of extra resources for expansion as you may add additional base monitors as your estate grows.
Perhaps most importantly: this does not and cannot take into consideration slow networks/WAN links. The speed of SQL Monitor is limited by the communication time with the slowest base monitor. In cases where this is too slow, we recommend using another web server.
Disk requirements
We recommend using high performance SSDs.
The amount of disk space required also depends on your data retention policy and whether your SQL Monitor database (data repository) uses a SIMPLE or FULL recovery model. Setting short data retention windows and using the SIMPLE recovery model will help to minimize disk space requirements.
SQL Server for the repository
We recommend using SQL Server Enterprise or SQL Server Standard. However, if you're using SQL Server Express, we recommend you set short data retention windows (1 week for data you want to view trends for, 3 days for troubleshooting data) and do not monitor more than 10-15 servers.
Example specifications
Here is a list of scenarios and appropriate specifications.
Scenario 1: 20-100 servers in one data center
For 20 servers or fewer, whilst in general we would recommend hosting the web server and base monitor on different host machines, adequate performance can often be achieved with one.
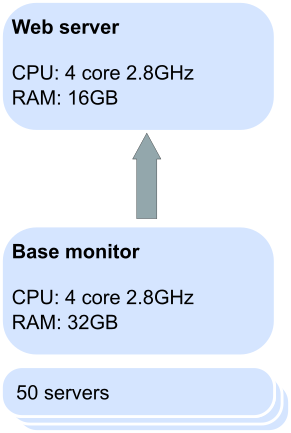
For 50 servers, we recommend separate machines for the web server and base monitor:
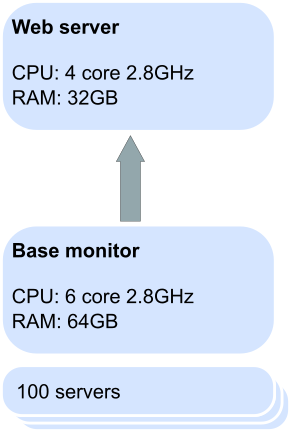
For 100 servers:
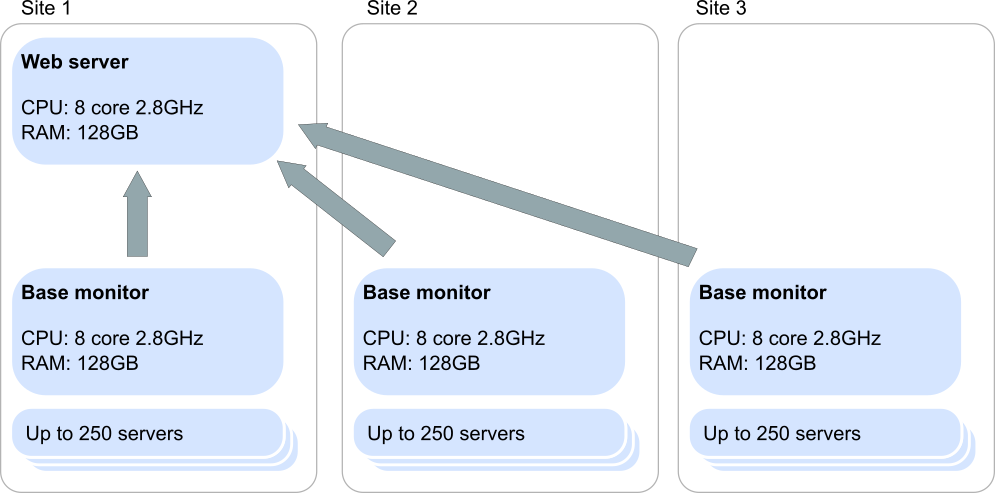
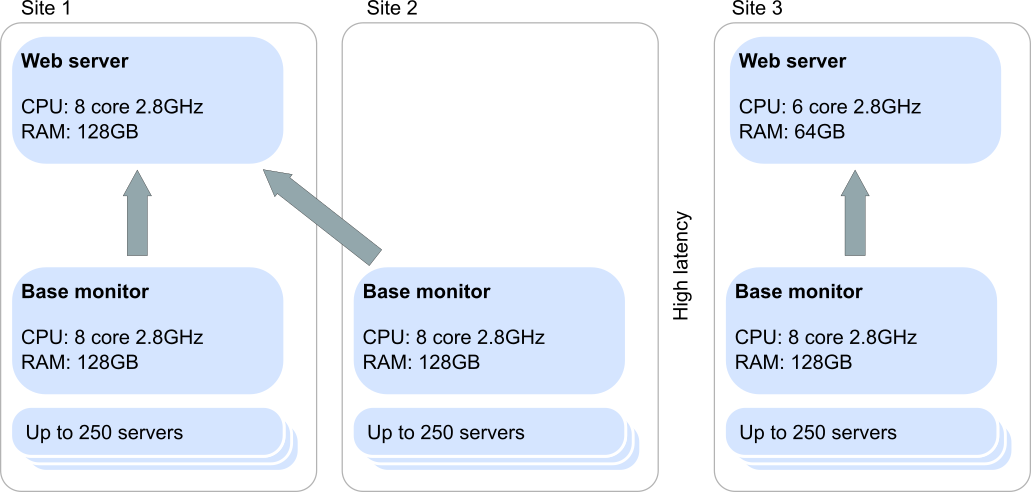
Scenario 2: Multiple data centers
In this scenario we have 3 connected data centers connected via high performance fiber. We recommend locating the website closes to the team using SQL Monitor the most, in this case Site 1:
Scenario 3: One data center has more than 250 servers
In this scenario we use more than one base monitor for a single data center.
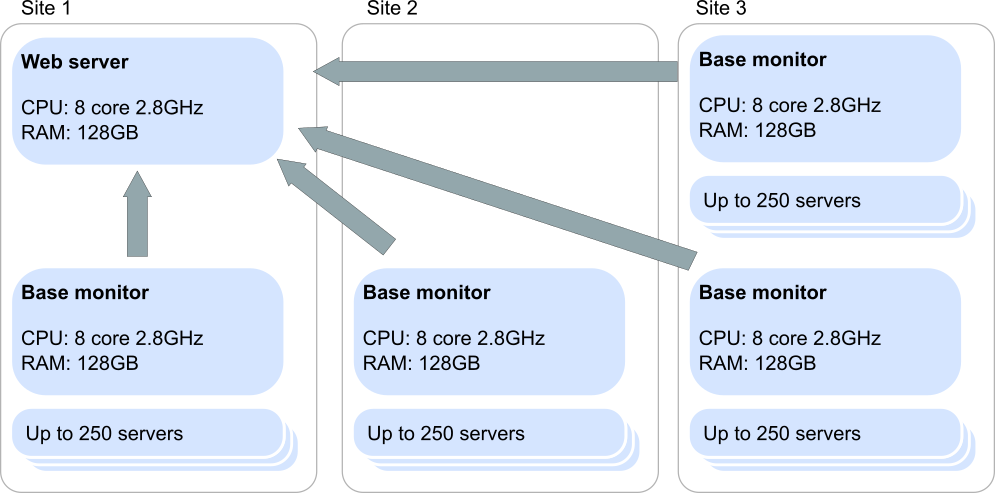
Scenario 4: Slow communication with one data center
In this scenario, one data center has a slow communication link, so we would recommend two installations of SQL Monitor: