Permissions required for the Redgate Monitor Service accounts
Published 28 March 2024
This section doesn't apply for Redgate Monitor SaaS, which is hosted and mainatined by Redgate. For SaaS specific information see Agents.
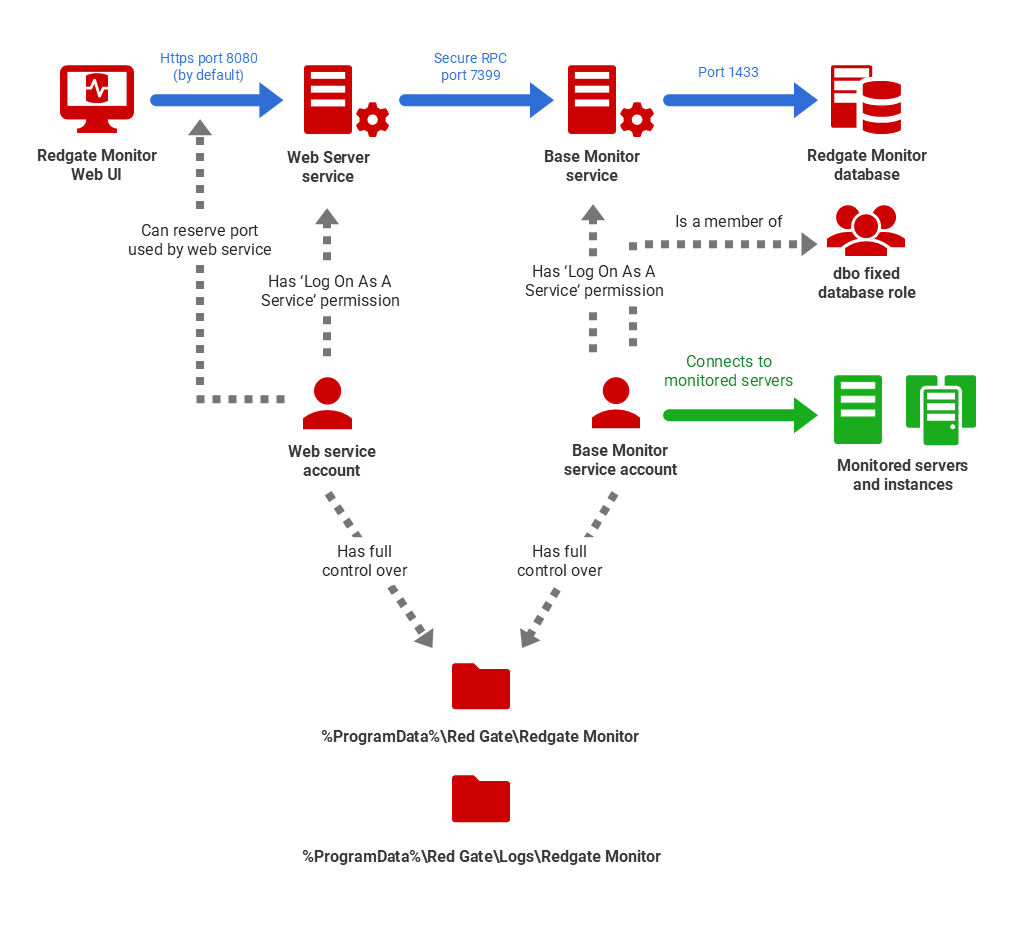
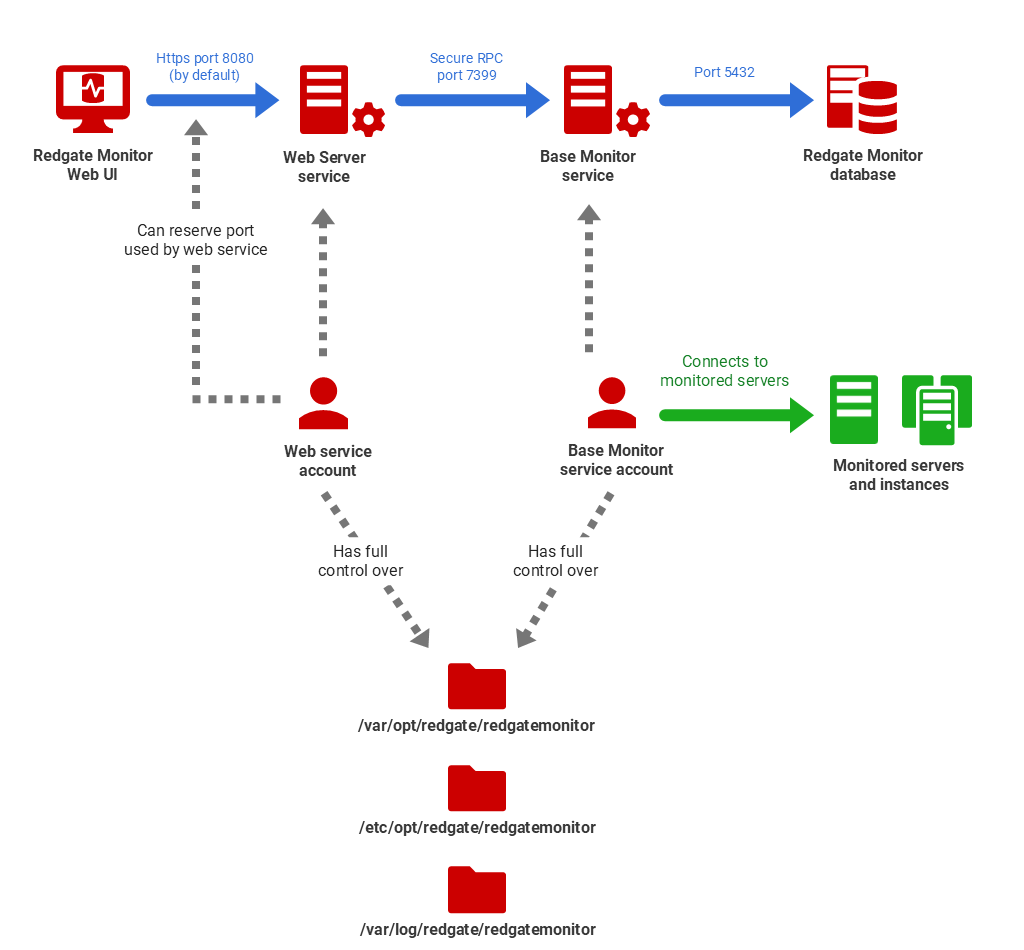
The following diagram depicts a 3-server installation of Redgate Monitor, shows the connections between the major Redgate Monitor components (blue arrows), and summarizes the permissions required for the Services accounts that will run the Base Monitor and Web Server services. The Base Monitor service will also need to connect to the servers and instances that it needs to monitor; this can use the Base Monitor service account or other accounts.
These are example set ups with default ports. Both Linux and Windows versions of monitor can use either an SQL Server or PostgreSQL with TimescaleDB as the Data Repository.
The Service account details are established initially as part of the Redgate Monitor installation process, but you can change the account used to run either service as described below. The following sections summarize the permissions each service account requires. For an understanding of why they need these permissions, see How Redgate Monitor works.
Web Service account requirements
The Web Server Service account requires the following permissions:
- The account should have Log on as service rights. For information on how to assign these permissions, see Add the Log on as a service right to an account.
- The account should have Full Control over the folder
%ProgramData%\Red Gate\Redgate Monitor. - The account should have Full Control over the folder
%ProgramData%\Red Gate\Logs\Redgate Monitor. The account should be able to reserve the port that the web service is configured to use. To do this, run in an admin command console on the server:
netsh http add urlacl url=http://*:<SqlMonitorPort>/ user=<myWebServiceAccount>
where <SqlMonitorPort> is the port you are using to access Redgate Monitor (it uses port 8080 by default, but you may well wish to change this), and <myWebServiceAccount> is the name of the Web Service Account.
- If HTTPS is configured, the account should have access to the SSL certificate.
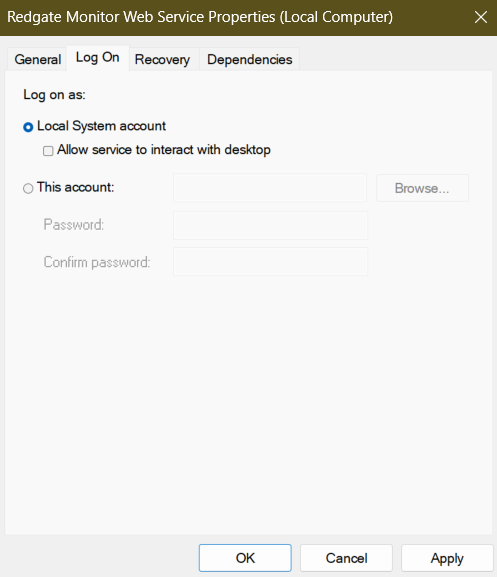
If you install the default Redgate Monitor Web Server, then after initial installation the Web Service account will be running as a Local system account (the LocalService account) to which Redgate Monitor will have granted the required permissions on the local machine, during installation. However, you can subsequently configure it to use a different account:
Any alternative account will need the previously listed permissions, either by its group membership or explicitly. If the account has membership of the local administrators’ (sysadmin) group then it will have the permissions by default. However, you may want to avoid this for security reasons, and all required permissions are relatively straightforward to establish.
The installation script will create the user redgatemonitor and assign appropriate permission to the installation, configuration, data, and log directories.
If you wish to use another user, it should have drwxr--r-- (read/write) access to:
- Installation directory:
/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor - Data directory:
/var/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor - Config directory:
/etc/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor - Log directory:
/var/log/redgate/redgatemonitor
And -rwxr-xr-x on (execute)
- Service:
/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor/base/RedGate.Monitor.BaseMonitor
Base Monitor Service account requirements
The Base Monitor Service requires access to one or more accounts to
- Run the service on the local machine
- Connect to the Redgate Monitor database
- Connect to remote servers that you wish to monitor
Run the service on the local machine
This is the Base Monitor Service account, and it requires the following permissions:
- The account should have Log on as service rights. For information on how to assign these permissions, see Add the Log on as a service right to an account.
- The account should have Full Control over the folder
%ProgramData%\Red Gate\Redgate Monitor. - The account should have Full Control over the folder
%ProgramData%\Red Gate\Logs\Redgate Monitor.
The installation script will create the user redgatemonitor and assign appropriate permission to the installation, configuration, data, and log directories.
If you wish to use another user, it should have drwxr--r-- (read/write) access to:
- Installation directory:
/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor - Data directory:
/var/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor - Config directory:
/etc/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor - Log directory:
/var/log/redgate/redgatemonitor
And -rw------- on (please note, this file contains connection strings so for security reasons we recommend that only the specific user has access to it)
- Configuration file: /etc/redgate/redgatemonitor/redgatemonitor.conf
And -rwxr-xr-x on (execute)
- Service:
/opt/redgate/redgatemonitor/web/RedGate.Monitor.WebService
Connect to the Redgate Monitor Data Store database
On initial install Redgate Monitor can be configured to either use SQL Server or PostgreSQL with TimescaleDB.
Privileges when using PostgreSQL with TimescaleDB as the Redgate Monitor Data Store
The Postgres User ID given to the Redgate Monitor installer needs to have the CREATE privilege on the database.
Permissions when using SQL Server as the Redgate Monitor Data Store
The account that the Base Monitor service uses to access the data repository is specified in the Connection Details section of the installer. It can be either the Windows service account or a SQL login account.
The account should have permissions below and roles on the Data Repository database (called RedGateMonitor by default).
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER sqlmonitor_user; ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER sqlmonitor_user; ALTER ROLE db_ddladmin ADD MEMBER sqlmonitor_user; GRANT EXECUTE TO sqlmonitor_user; GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO sqlmonitor_user;
When installing the first time, not upgrading an existing installation, the account will also require the below permission. You may revoke this permission after the installing and running the base monitor for the first time. The upgrades and day-to-day operations will not require it. If you do not grant this permission to the account, when you run Monitor after a fresh installation, you will get an error and will not be able to start Monitor. To fix this, just grant the permission and re-run Monitor.
GRANT ALTER TO sqlmonitor_user;
The account will require the additional permissions below for the actions mentioned; but these requirements are optional. Please find more information on the performance settings you can use here.
GRANT ALTER TO sqlmonitor_user; -- Setting delayed durability feature on/off GRANT ALTER ANY DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION TO sqlmonitor_user; -- Setting query optimizer hot fixes on/off
- Alternatively, the account can be a member of the db_owner database role. This is the role that will be granted automatically if you create the Data Repository through the installer. If you want to provide a lower permission account, make sure to provide an existing database that has an account configured as described in above steps.
- If the data repository is hosted on Azure SQL Database, then a user should be created on the master database for the login you are trying to use in the installer.
If you choose SQL Server authentication, then the Base Monitor service will run as a Local system account (the LocalService account) to which Redgate Monitor will have granted the required permissions (see above) during installation.
If you choose Windows authentication, with a Windows / Active Directory domain account, then this account will also be used to run the Base Monitor service and it will need the required permissions to do this (outlined above).
Connect to remote servers that you wish to monitor
For more information see: Adding servers for monitoring.
Permissions for monitoring SQL Server from a Windows Base Monitor
The Base Monitor service will need access to one or more accounts with adequate permissions required for monitoring SQL Servers.
If you specify a Windows / Active Directory domain account to run the Windows Base Monitor service, this account can be used to grant access to monitored servers. This can simplify the management of passwords when adding servers. However, you can also supply one or more separate accounts for these purposes.
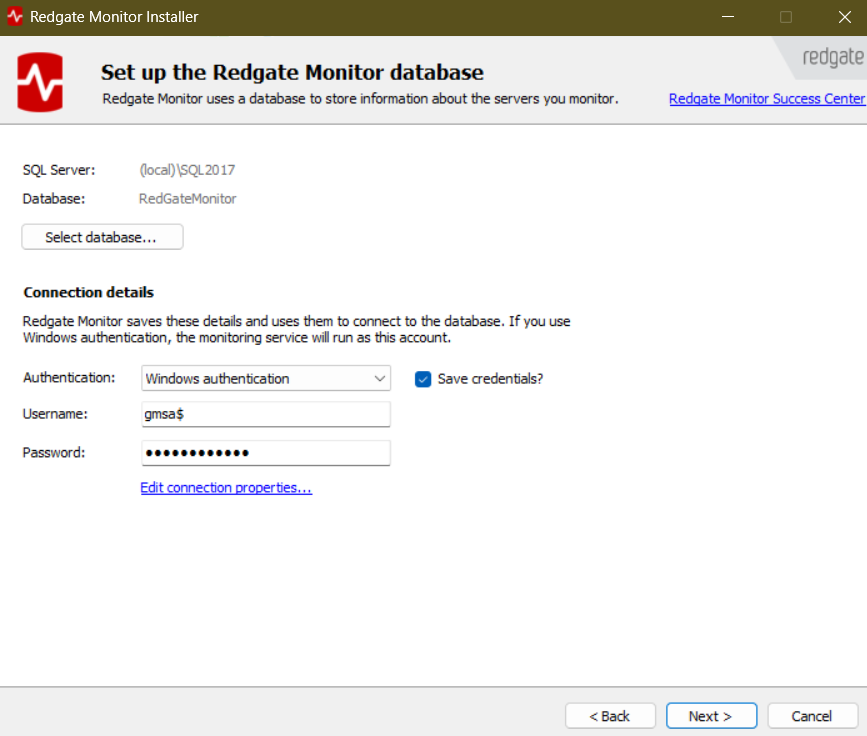
Group Managed Service Accounts
Redgate Monitor supports the use of a group Managed Service Account (gMSA) for the Base Monitor service. If you use a gMSA account to run the Base Monitor, the gMSA can be used to give Redgate Monitor access to monitor servers. To specify a gMSA during installation, simply enter the gMSA name with a dollar-mark ($) on the Installation options page: