Choosing between layouts
Published 28 August 2014
You can lay the diagram out in the following ways:
This page explains what each layout does, and the advantages and disadvantages of each layout.
Circular
The circular layout lays the objects out to form the boundaries of circles, with connections that cross the centre of the circle.
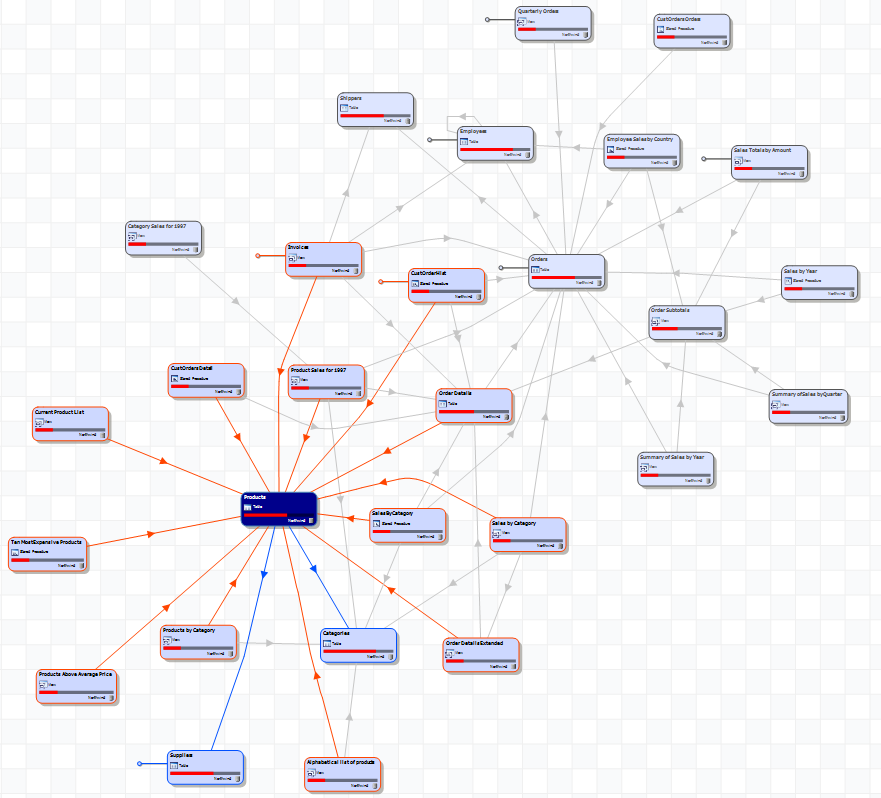
Hierarchic
The hierarchic layout organizes the objects in a hierarchical structure, where objects are placed in tiers above the objects they reference.
Orthogonal
The orthogonal layout places objects so that the lines between objects are as close to vertical and horizontal as possible.
This is best for diagrams that don't contain many objects.
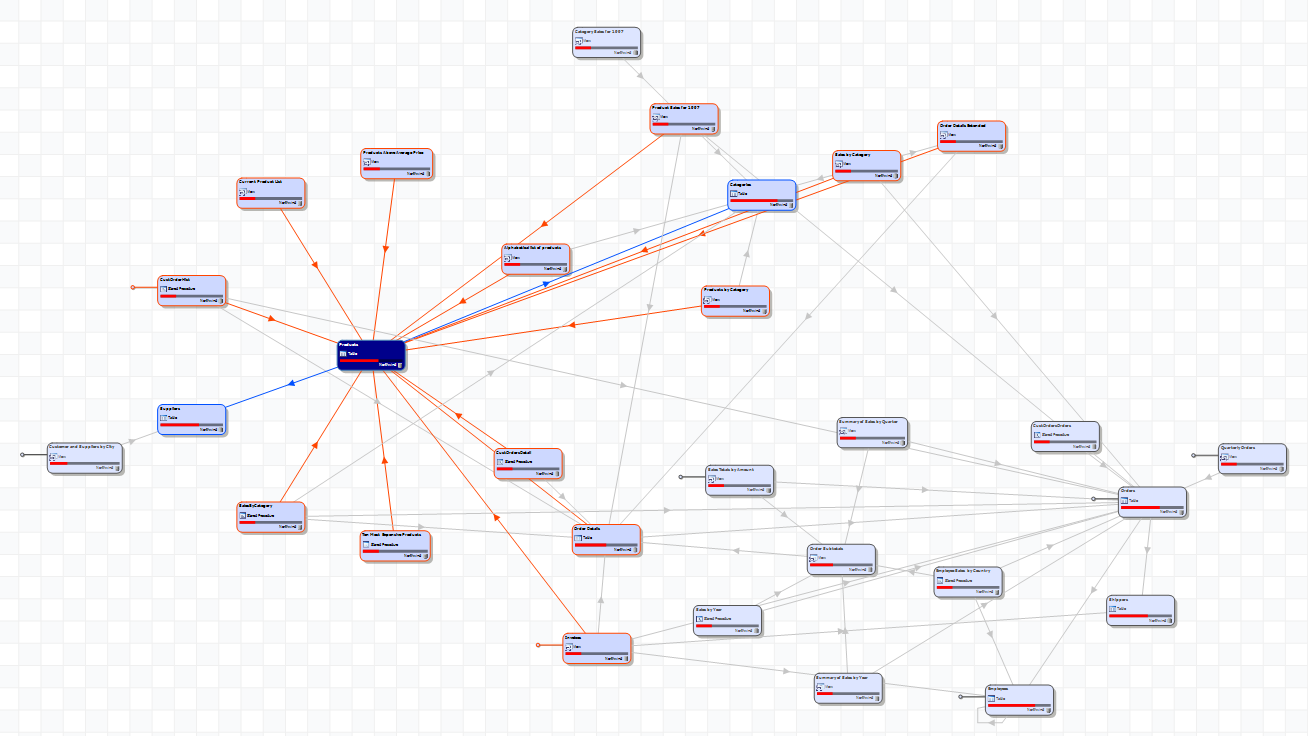
Smart organic
The smart organic layout links objects into sets of clouds or lattices.
This layout is good for grouping related objects together.
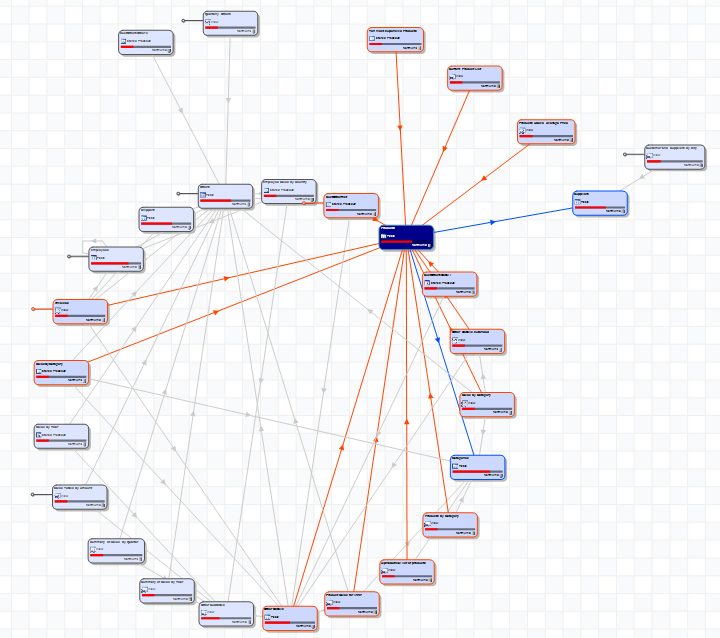
Balloon tree
The balloon tree layout groups related objects together in balloon-like clusters. It is the default layout.
This layout is good for grouping related objects together, and is suitable for diagrams that contain lots of objects.