Architecture Diagram
Published 04 February 2023
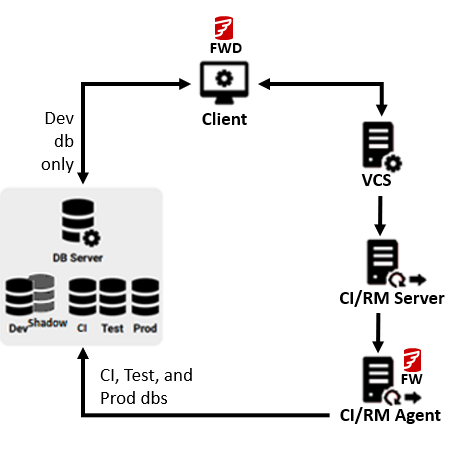
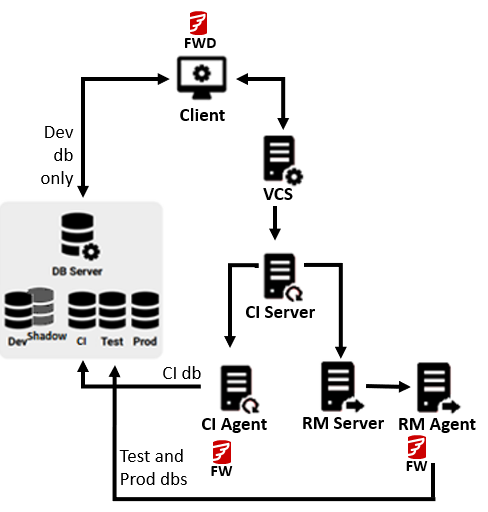
One system | Different systems for Continuous Integration (CI) and Release Management (RM) |
|---|---|
Legend: Flyway Desktop (FWD) - Version control your database objects, generate migration scripts and validate deploymentsClient machine - This is where the developer works. This machine needs to be able to access the development database (e.g., using your database IDE) and the Version Control System (VCS) (e.g., using a VCS client like GitHub Desktop or Sourcetree). This is where Flyway Desktop is installed.
Using Docker is recommended because the image comes with all the prerequisites and nothing needs to be installed/maintained on your agents. | |
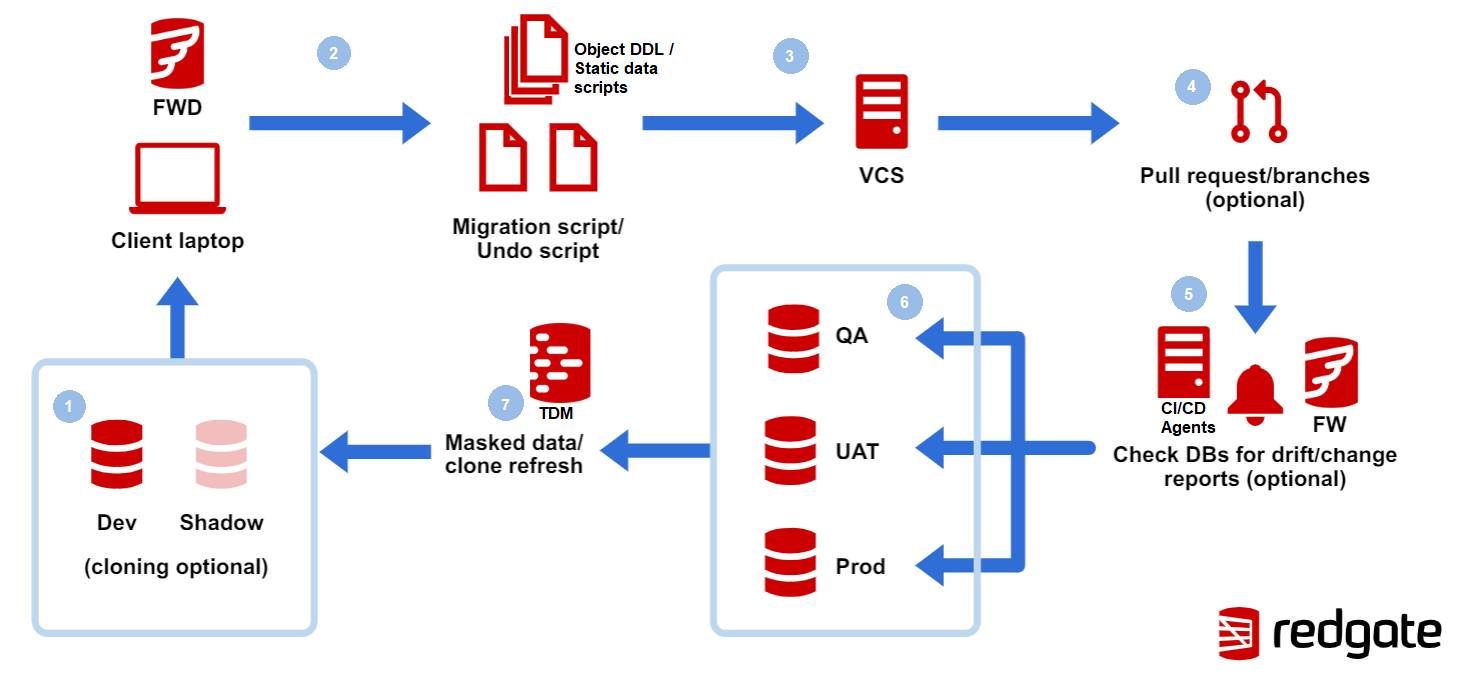
Sample Process Workflow - Database development and deployment with Flyway Enterprise
Starting in the bottom left:
- Work directly against your development database in your preferred IDE.
- In Flyway Desktop, see what has changed. Save the object level and static data SQL scripts to disk.
- Optional - If you wish to use migration scripts for deployments, generate versioned and undo migration scripts on disk.
- Use Flyway Desktop or your own VCS client to version control these scripts.
- Optional - Create a Pull Request (PR) so the database changes and optional migration scripts are reviewed. Code analysis and database unit testing can be ran to catch issues early.
- Optional - Use your CI/CD system to generate a report of changes, check for drift (changes that happened outside the pipeline, e.g., hot fix), run code analysis and other testing (unit, integration, performance, etc.).
- Use your CI/CD system to deploy your database changes to your downstream environments (QA, UAT, Prod). Optional - Set up a manual intervention before going to Prod, so releases can be reviewed and pushed on your time.
- Optional - Refresh your development database using Redgate Test Data Manager (TDM) with realistic production-like datasets, while keeping your prod data safe.
- Repeat step 1.
For automated deployments Flyway is designed to fit seamlessly into your existing CI/CD infrastructure allowing you to automate database deployments. All that is needed is for Flyway to be installed onto your CI/CD build agents which will be used to run your pipelines. In the event that you have agent pools which provide high availability or failover then Flyway will need to be present on all of the agents that could run the pipelines which include Flyway actions.
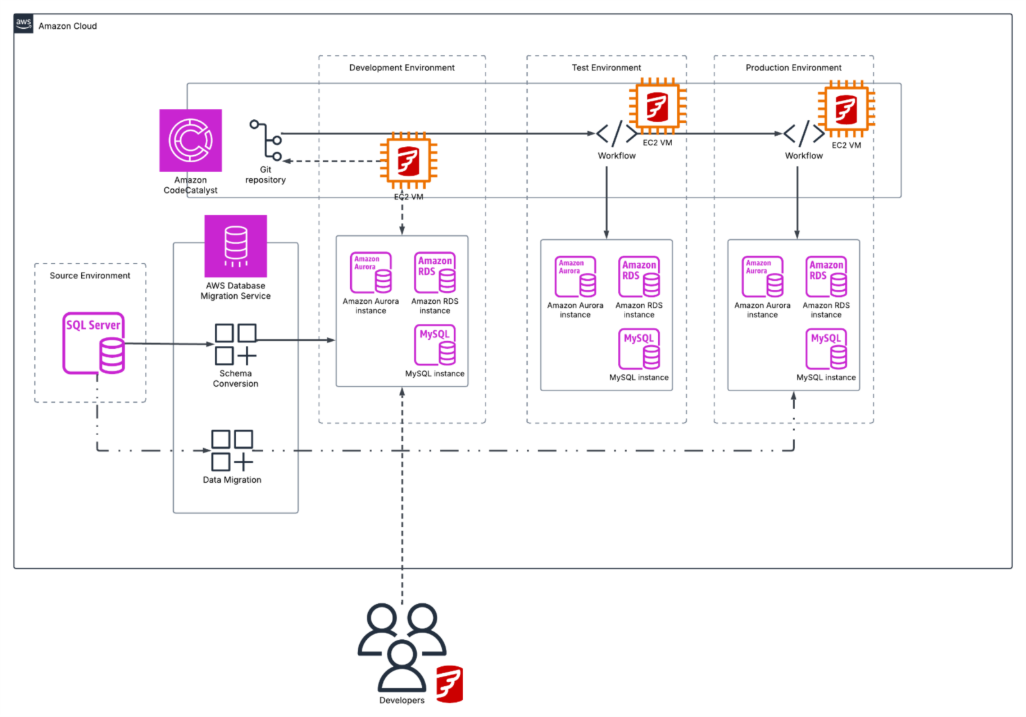
The following diagrams look at how Flyway can be deployed within an AWS environment to support the automated deployment of database changes by teams. Flyway is made up of two components, the CLI tooling which is used for automation of script generation and the state-based or migration-based delivery of database changes. The other component is the Flyway Desktop tool which is used by developers to manage the Flyway projects, interact with source control, and manage database scripts.
The Flyway CLI tooling can be deployed into EC2 VMs or into containers, these can then be used to connect to the different database systems which are involved in the development and deployment process. This can be automated with CI/CD agents, job scheduling solutions, or ad-hoc with the CLI.
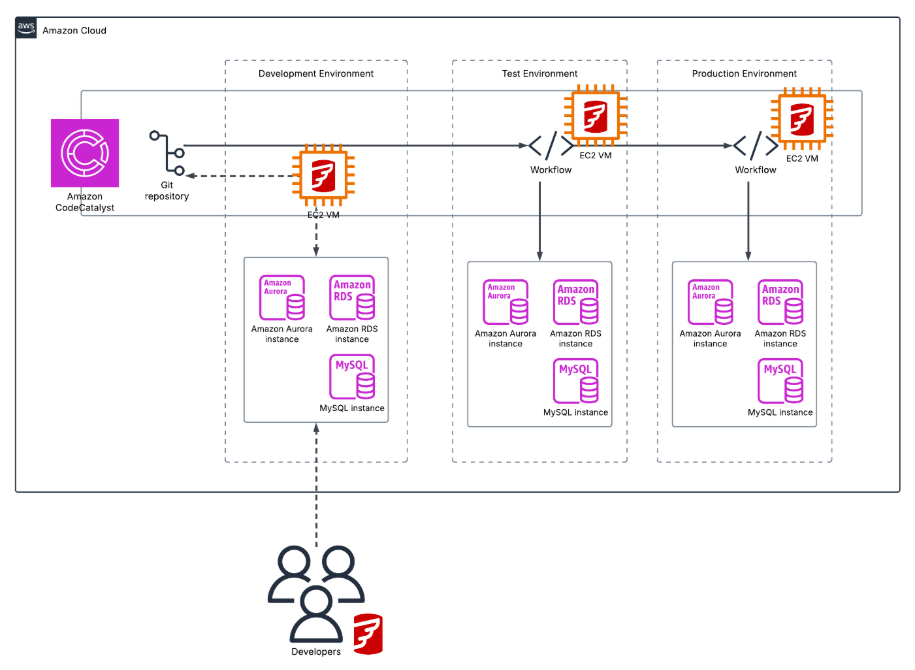
Flyway deployment as part of workload migration and modernization with AWS DMS and CodeCatalyst. This illustrates how Flyway can work in combination with AWS services to help with homogeneous and heterogeneous migrations where there is additional work that needs to be completed by developers to update code in the database as part of the migration or modernisation activity.
This shows Flyway deployed in conjunction with Amazon CodeCatalyst where developers can update their development databases then use Flyway to generate the migration scripts, add them to a Git repository and then have CodeCatalyst Workflows deploy the changes test and production.
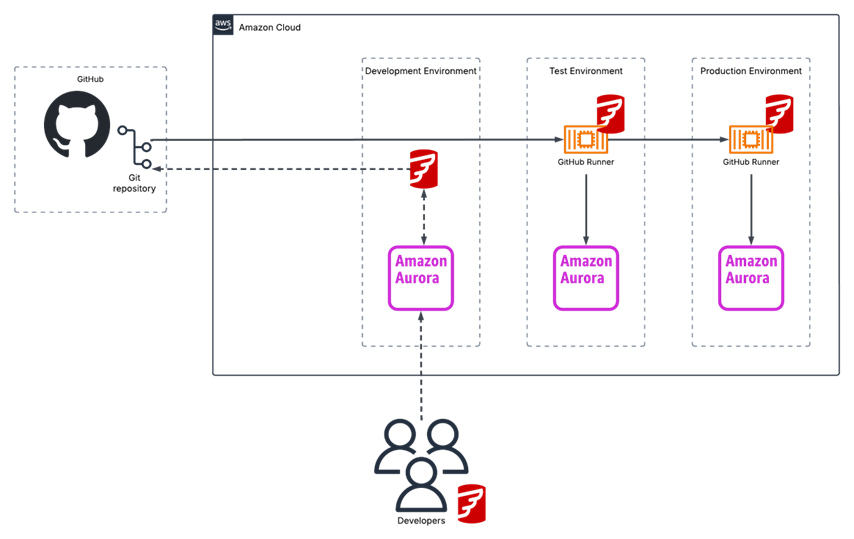
Flyway deployed with GitHub as Repo and CI/CD platform deploying to Amazon Aurora databases.
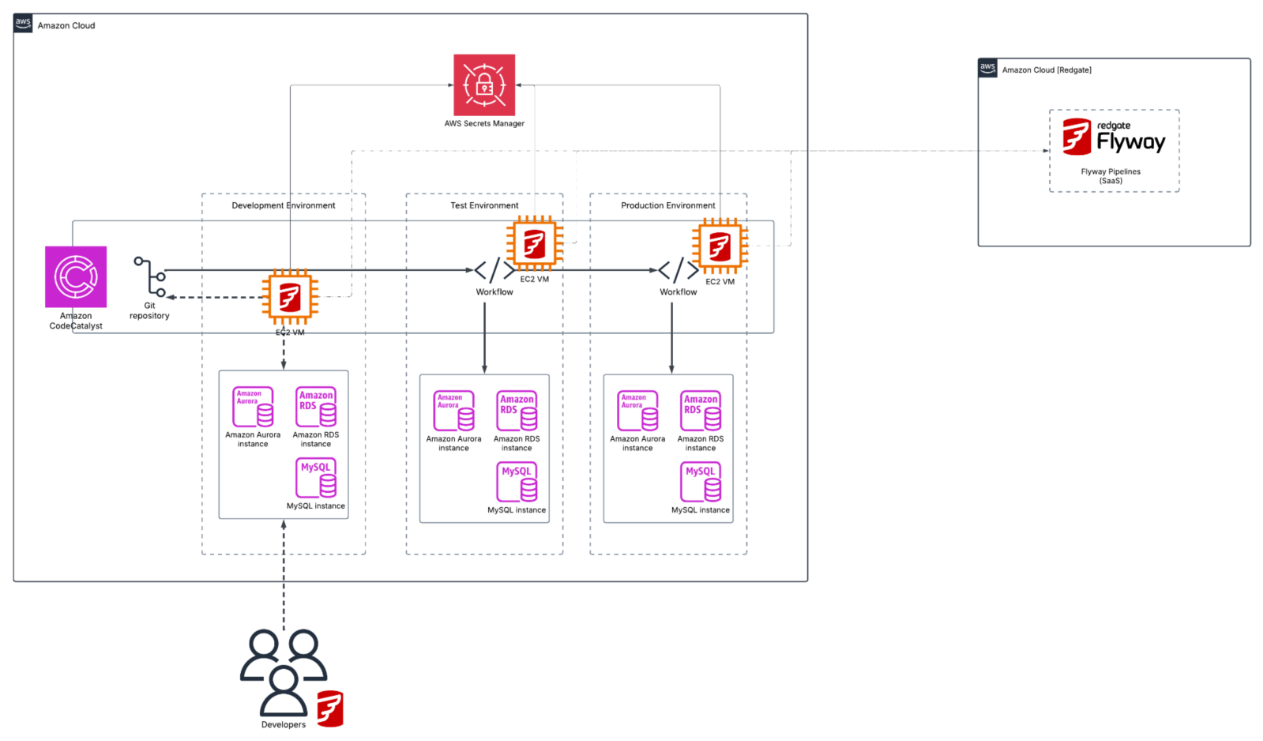
Flyway components connecting to AWS Secrets Manager in customer account for secret management. Connectivity to Flyway Pipelines (Free SaaS Flyway component hosted in our AWS Account) providing dashboards showing Flyway deployment metrics.
Next steps:
- Watch our Redgate University Courses
- Download the installers
- Follow the Flyway Implementation Checklist